Trong cuộc sống hàng ngày, chắc hẳn các bạn cũng đã quen thuộc với các giải pháp xác thực bằng các loại phương thức khác nhau: ví dụ xác thực OTP, xác thực bằng mật khẩu, xác thực bằng sinh trắc học thiết bị, xác thực liveness thực thể sống, xác thực Soft OTP,…
Hôm nay mình sẽ chia sẻ lại cách mình xây dựng một giải pháp xác thực giao dịch hoàn chỉnh, thoả mãn các yêu cầu đề ra cho việc tái sử dụng, mở rộng cao, dễ chỉnh sửa, bảo mật tốt.
Ngoài ra còn là cơ sở và tiền đề cho việc nâng cấp các luồng xác thực giao dịch cũ sử dụng phương pháp xác thực mới này nếu có nhu cầu chuyển đổi.
Oke trước tiên các bạn hãy cùng tìm hiểu hiện trạng vấn đề nhé.
Mục Lục
Hiện trạng vấn đề
Trong hệ thống cũ của bên mình, hiện tại đang chia làm 2 loại hình giao dịch:
Giao dịch phi tài chính
Giao dịch phi tài chính là những giao dịch không liên quan đến chuyển động dòng tiền, chủ yếu là những giao dịch truy vấn, cập nhật thông tin, luồng nghiệp vụ hỗ trợ,…
Có một số API chuyên làm những nhiệm vụ kiểu: xác thực mật khẩu, xác thực sinh trắc học thiết bị, xác thực mã OTP,…
Ví dụ: sau khi thực hiện một xong một chức năng cụ thể như đổi từ thiết bị A sang thiết bị B, các bạn sẽ cần phải thực hiện một phương thức xác thực như OTP hoặc BIO_2345 (sinh trắc học) để đảm bảo bạn là chủ sở hữu thiết bị đó.
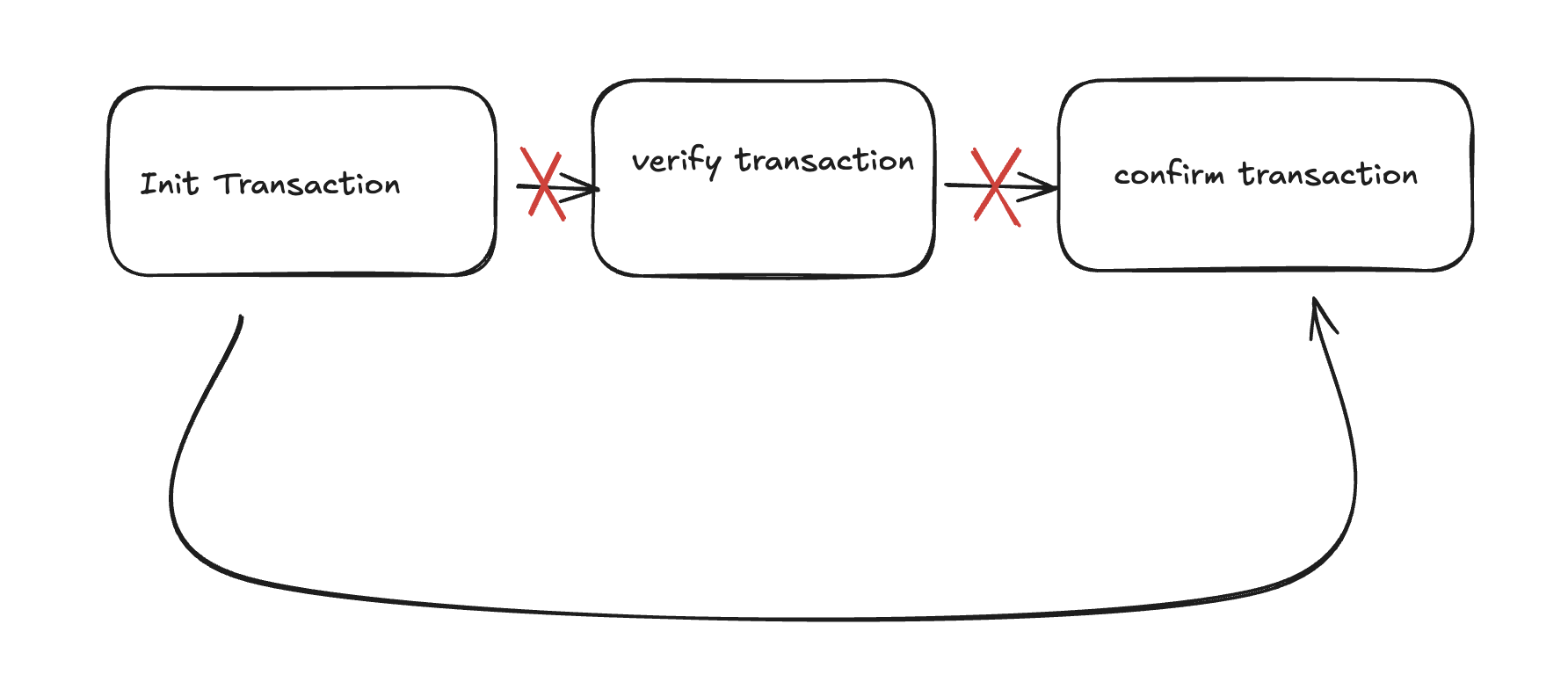
Tuy nhiên trong trường hợp bị lộ API ra ngoài, hacker có thể thực hiện nhiều thao tác khác liên quan đến luồng nghiệp vụ chính mà bỏ qua bước xác thực, vì hiện tại những API đó là “stateless” và không được liên kết với một ngữ cảnh giao dịch cụ thể nào cả.
Hạn chế của những API kiểu này là bảo mật kém, nó chỉ có làm 1 nhiệm vụ duy nhất là thực hiện xác thực theo đúng nghĩa đen: ví dụ xác thực mật khẩu của ông A là hợp lệ, xác thực otp khách hàng là nhập đúng,…

Các bạn cứ hiểu rằng là, lớp xác thực sinh ra như 1 cái ổ khoá giữ nhà, buộc bạn phải tra đúng chìa thì mới mở được ổ khoá đó, nhưng giờ bạn không cần tra chìa khoá vào ổ nữa mà vẫn mở được cửa thì tình trạng gì sẽ diễn ra?
Giao dịch tài chính
Giao dịch tài chính là toàn bộ những giao dịch liên quan đến tiền, phát sinh thay đổi ghi nợ, ghi có vào tài khoản: ví dụ nạp tiền, rút tiền, chuyển tiền, thanh toán,….
Các giao dịch tài chính hiện tại được thiết kế theo từng luồng nghiệp vụ và đã đảm bảo cơ chế bảo mật tốt, tuy nhiên là không có tính tái sử dụng và không đồng nhất.
Giả sử nếu sau này phát sinh thêm một luồng thanh toán đặc biệt so với những luồng hiện tại thì sẽ phải clone ra nhiều đầu API xác thực giao dịch riêng tương ứng với luồng.
Điều này dẫn tới sự hạn chế về mặt phát triển, maintain, code trùng lặp nhiều và khá khó tái sử dụng.
Nhớ lại hồi tháng 7 năm 2024 mình code phần xác thực sinh trắc học giao dịch để đáp ứng quyết định 2345 của Ngân Hàng Nhà Nước, tự nhiên nghĩ lại thấy ngại thật, giá mà đợt đó có sẵn luồng thiết kế chuẩn để đáp ứng cho tất cả các nghiệp vụ thì hợp lý biết mấy.
Các tiêu chí cần đạt được của giải pháp xác thực
Nhân tiện vừa rồi bên mình vừa mới phát triển thêm một luồng xác thực phi tài chính mới (mở tài khoản ngân hàng S**), nếu mà vẫn dùng lại những API bảo mật kém từ trước thì chắc chắn sẽ không vượt qua được phần Pentest của team an toàn bảo mật.
Mặc dù đội BA/PO có thể thông báo với team ATBM rằng: giao dịch phi tài chính thì có thể cho phép chấp nhận rủi ro và cho golive. Tuy nhiên, đứng ở góc độ kĩ sư phần mềm thì mình thấy việc để lộ lọt dữ liệu, rò rỉ bảo mật ở những luồng mình làm là một điều không nên.
Thế nên là, triển khai xây dựng giải pháp mới luôn thôi, không ai chịu làm thì mình làm.
Mục tiêu của kiến trúc
Kiến trúc của giải pháp xác thực cần phải đáp ứng được những tiêu chí cơ bản sau đây:
- Đảm bảo mọi bước xác thực đều được thực thi đúng thứ tự và nằm trong một “phiên” (session) giao dịch duy nhất, có giới hạn thời gian. Không thể bỏ qua bước, và không cho phép xử lý lặp lại.
- Cho phép cấu hình động các luồng xác thực cho từng loại nghiệp vụ mà không cần thay đổi code, ví dụ luồng A có hai phương thức, luồng B chỉ một phương thức, luồng C lại cần ba phương thức liên tiếp nhau chẳng hạn.
- Cho phép các phương thức được thay thế lẫn nhau, vì sẽ có nhiều loại phương thức được gọi là tương đương: ví dụ PASSWORD tương đương BIOMETRIC và ngược lại, OTP tương đương SOFT_OTP,….
- Xác thực được tập trung và có thể được sử dụng bởi bất kỳ luồng nghiệp vụ nào (mở tài khoản, rút tiền, chuyển tiền,…)
- Phải rất linh hoạt trong việc cấu hình, cho phép bỏ phương thức này, thêm phương thức khác.
Thiết kế
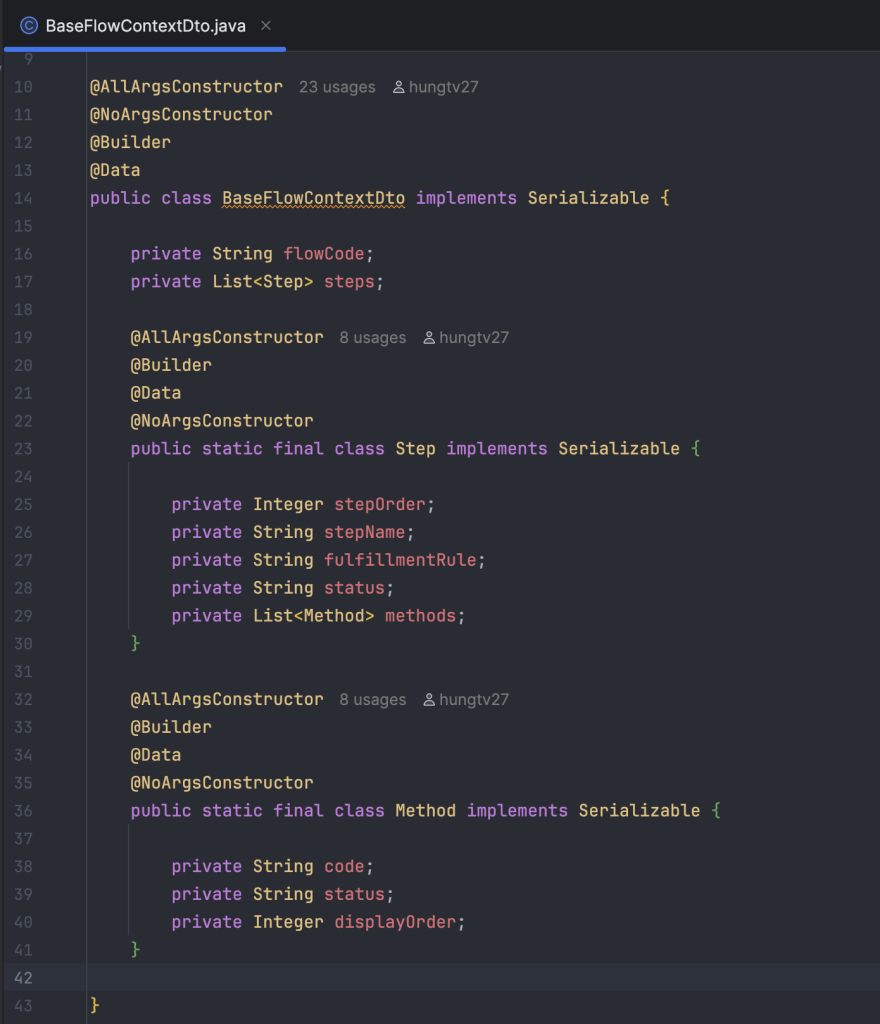
Mình định nghĩa một quá trình xác thực giao dịch là Flow, ở trong một flow của một phiên cụ thể sẽ được định danh bằng một mã uuid, trong flow sẽ có nhiều bước xác thực, trong mỗi bước xác thực sẽ bao gồm nhiều phương thức xác thực.
Để xác định được phiên cho từng user đối với từng luồng cụ thể, trước tiên các bạn cần phải xây dựng được một cái base flow trước, cùng xem chuỗi JSON bên dưới mình định nghĩa một cấu trúc chuẩn cho một luồng, ở đây là luồng mở tài khoản thanh toán ngân hàng S**.
{
"flowCode": "OPEN_ACCOUNT_S**",
"steps": [
{
"order": 1,
"name": "Bước xác thực đầu tiên",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
},
{
"order": 2,
"name": "Bước xác thực thứ hai",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC_C06",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
}
]
}Giải thích các trường dữ liệu:
flowCode: đại diện cho một luồng nghiệp vụ cụ thể cần đến phương thức xác thực.
steps: đây là một mảng khai báo các bước tuần tự, các bạn có thể khai báo luồng gồm nhiều bước tuần tự nhau, ở đây ví dụ mình cấu hình step 1 có hai phương thức xác thực là PASSWORD và BIOMETRIC (hai phương thức này có thể thay thế nhau dựa vào fulfillmentRule), step 2 có hai phương thức là BIOMETRIC_C06 và PASSWORD (hai phương thức này cần phải thực hiện đầy đủ).
order: thiết lập thứ tự thực hiện của step, các step cần được khai báo thứ tự ưu tiên khác nhau.
fulfillmentRule: trường này dùng để thiết lập rule xác thực trong 1 step, trong mỗi step sẽ có định nghĩa cho phép người dùng cần phải xác thực hết các phương thức (VERIFY_ALL) hoặc chỉ cần xác thực 1 trong các phương thức (VERIFY_ONE).
status: trạng thái của step, ví dụ nếu đã thực hiện xong hết các bước xác thực của step, thì trạng thái sẽ được cập nhật sang VERIFIED.
methods: đây là mảng khai báo các phương thức xác thực ở trong một step, các phương thức được cấu hình thứ tự thực hiện trên trường displayOrder, khi một phương thức được xác thực xong sẽ được chuyển trạng thái từ PENDING sang VERIFIED.
Q&A
Câu hỏi 1: Tại sao lại cấu hình hai phương thức giống nhau ở hai step khác nhau?
Đơn giản là vì mình muốn khai báo như thế để mọi người hiểu rằng, thiết kế này đáp ứng được cho việc cấu hình nhiều phương thức lặp lại khác nhau, có thể cấu hình phương thức giống nhau ở nhiều step khác nhau đều được.
{
"flowCode": "OPEN_ACCOUNT_S**",
"steps": [
{
"order": 1,
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
},
{
"order": 2,
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
},
{
"order": 3,
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
}
]
}
Nhưng thật ra thì, chẳng ai cấu hình trên production như thế kia làm gì cả, nó không phù hợp với thực tế và gây khó hiểu cho người dùng, chỉ đơn giản là thiết kế của mình đáp ứng được cho việc xác thực lặp lại nhiều phương thức giống nhau, đơn giản vậy thôi.
Câu hỏi 2: hai phương thức PASSWORD đều ở hai step khác nhau thì khi người dùng xác thực, làm sao để họ biết rằng đang xác thực PASSWORD cho step nào?
Ở một thời điểm người dùng chỉ được phép xác thực một phương thức cho một step, ví dụ khi thực hiện PASSWORD sẽ cần xác định được rằng họ đang thực hiện xác thực cho step 1 chứ không phải step 2, nhưng để xác định được step chính xác, các bạn sẽ cần dựa vào trạng thái của step khi xác định flow cho người dùng.
Các bạn cứ hình dung là, step 1 sẽ được đổi trạng thái sang PROCESSING khi người dùng khởi tạo một flow, ở một thời điểm chỉ có 1 step ở trạng thái PROCESSING mà thôi, vậy nên khi người dùng xác thực họ sẽ luôn tìm đúng được step mà mình cần xác thực, tránh tìm nhầm lẫn.
{
"flowCode": "OPEN_ACCOUNT_S**",
"steps": [
{
"order": 1,
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PROCESSING",
"methods": [
{},
{}
]
},
{
"order": 2,
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{},
{},
{}
]
}
]
}Thiết kế ERD
Vì lý do bảo mật nên mình sẽ không chia sẻ toàn bộ code thực tế trong dự án, tuy nhiên mình sẽ dựng lại toàn bộ code mẫu tuân thủ theo đúng tư tưởng thiết kế mà mình đã làm nhé.
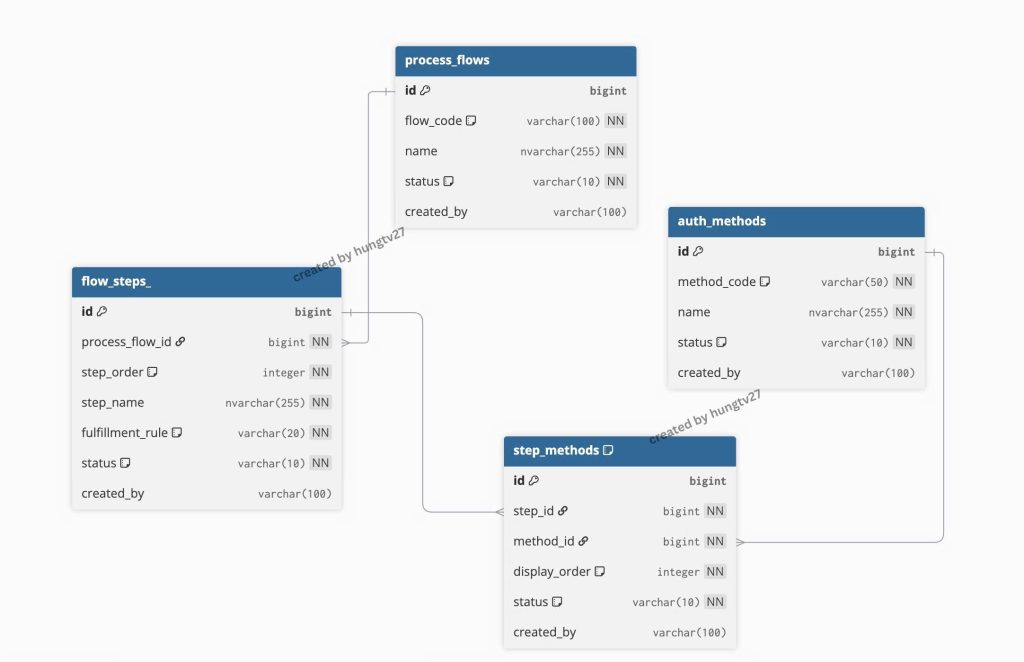
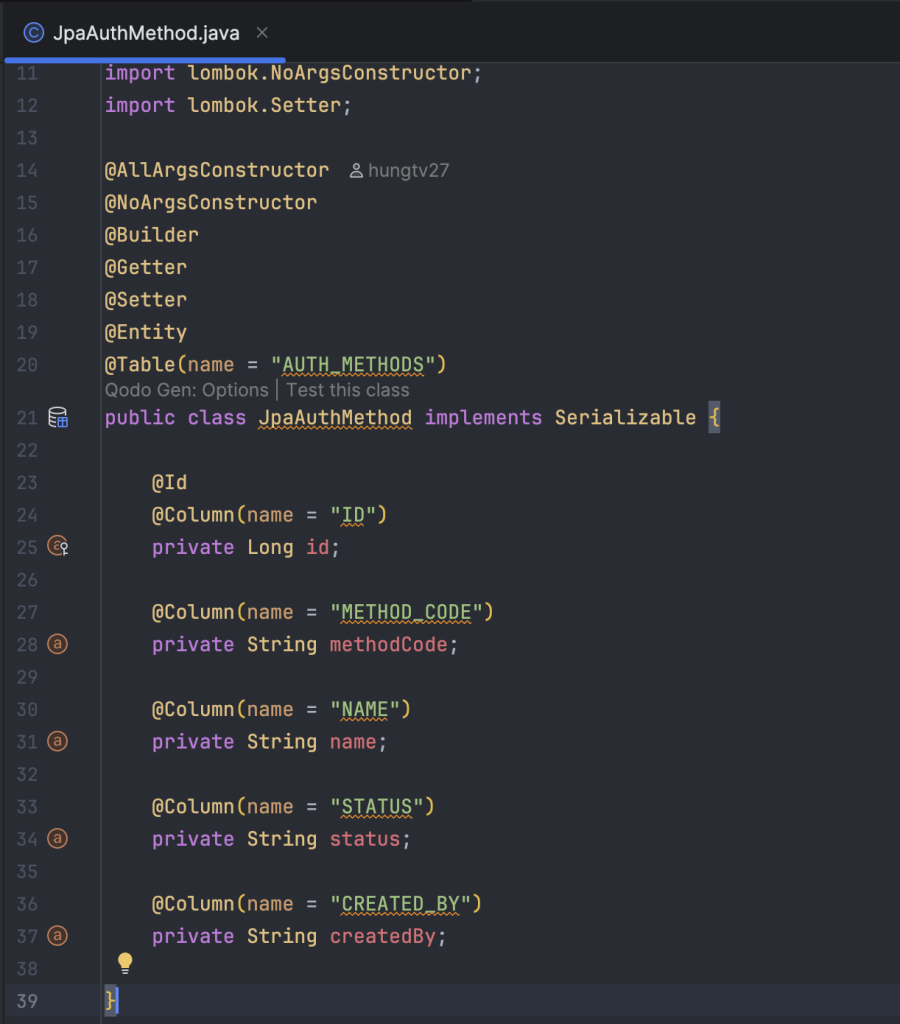
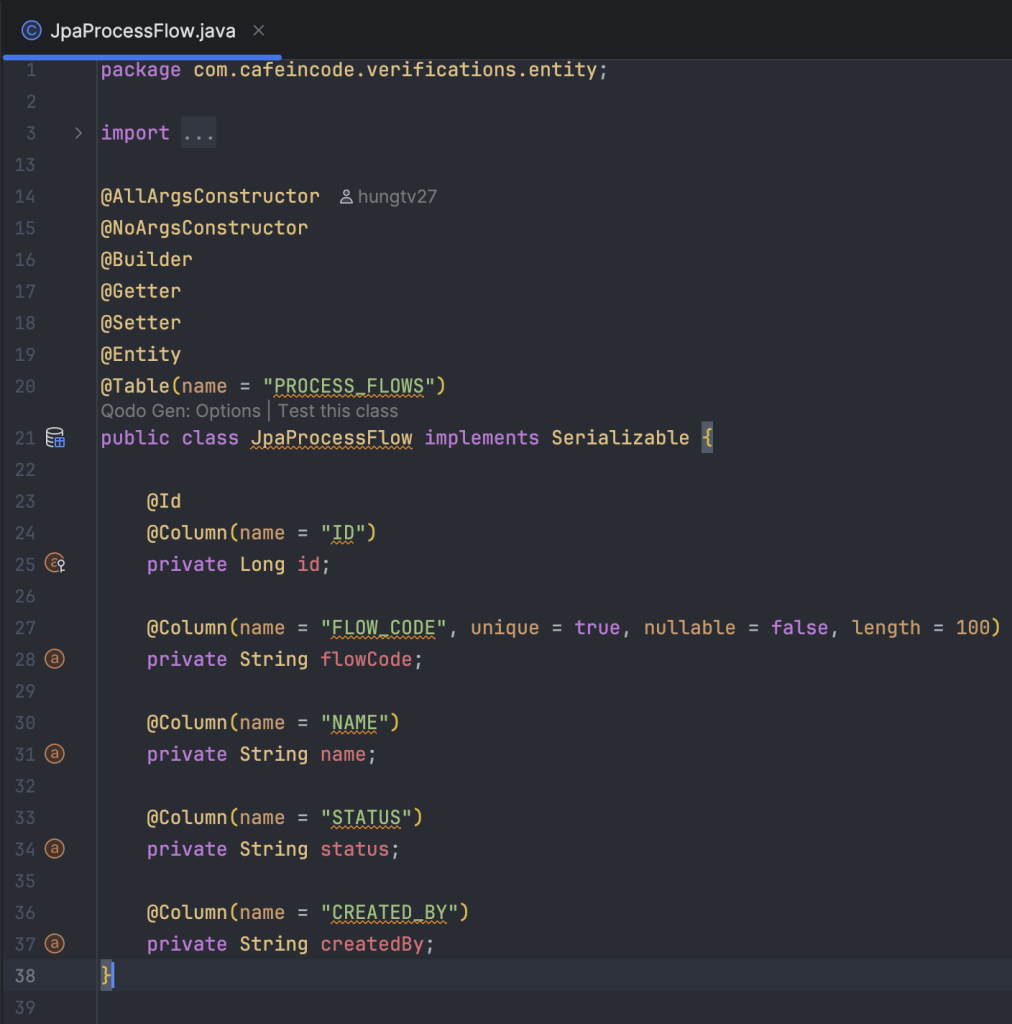
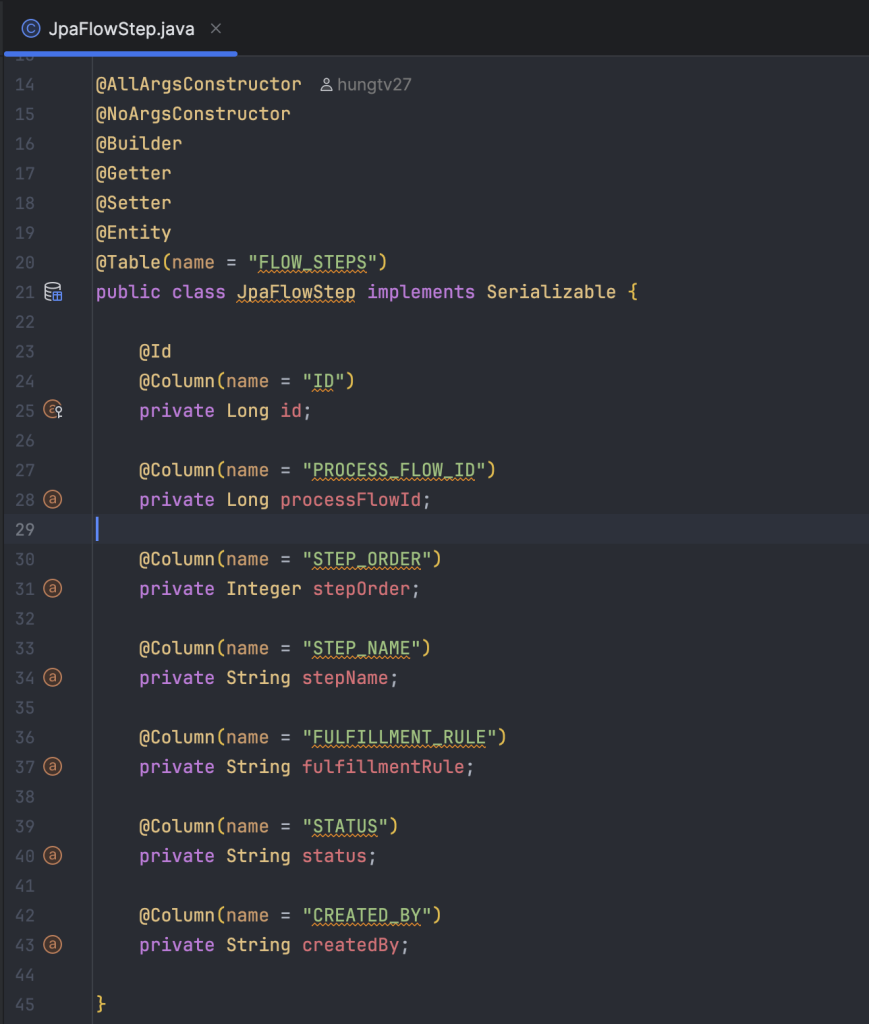
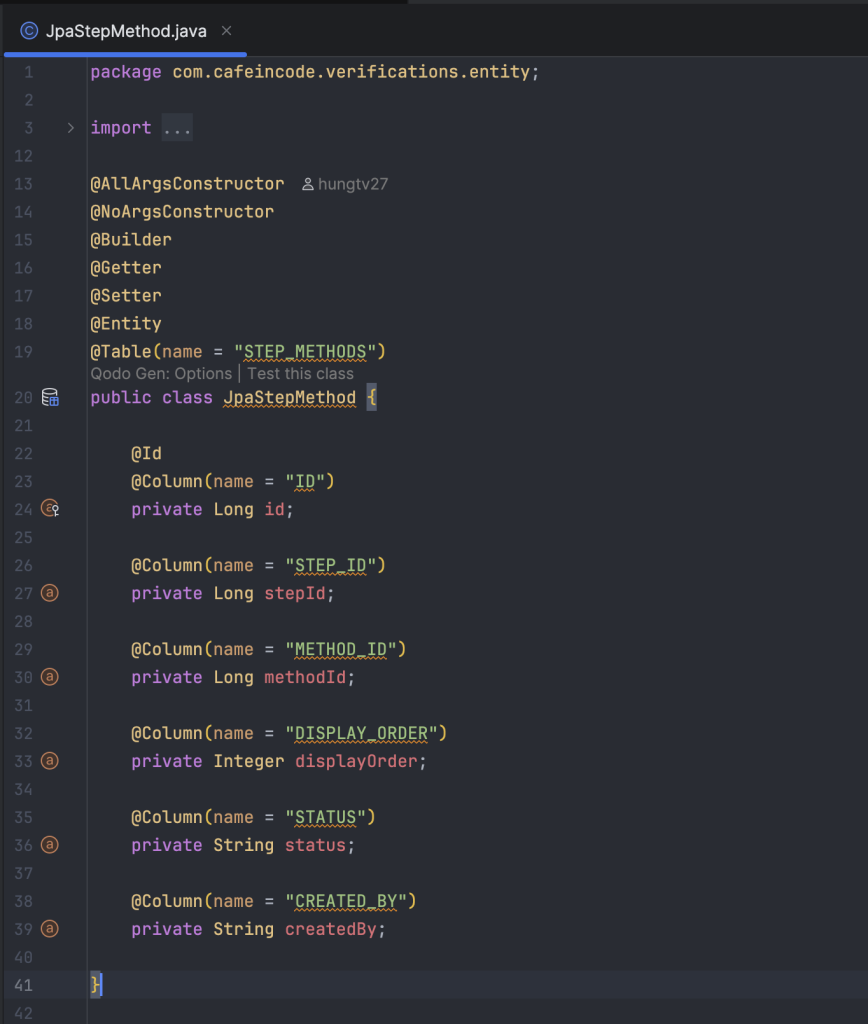
Trong thiết kế này của mình sẽ gồm bốn bảng sau:
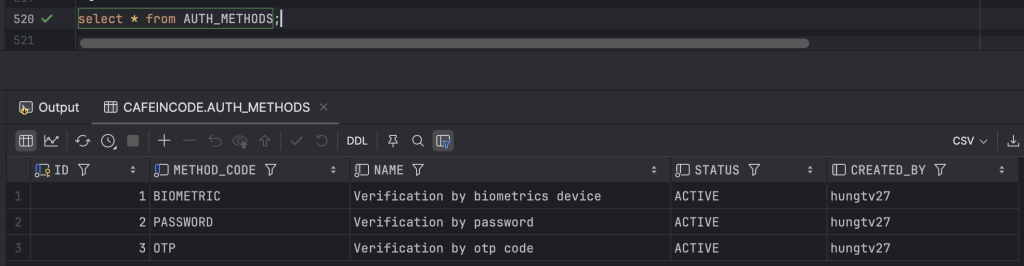
auth_methods: dùng để cấu hình tĩnh danh sách các phương thức xác thực, bao gồm: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC, OTP,…
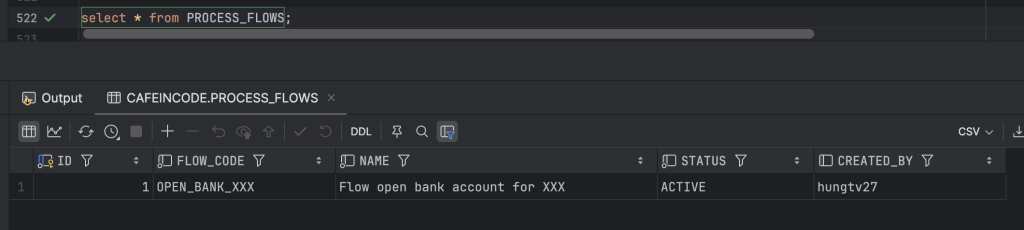
process_flows: khai báo các luồng nghiệp vụ, ví dụ OPEN_BANK_ABC, WITHDRAW, DEPOSIT,…
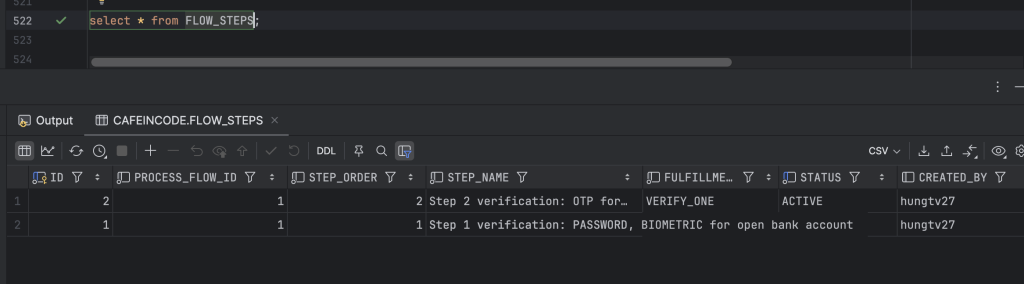
flow_steps: bảng này định nghĩa số lượng step của một luồng nghiệp vụ tương ứng ở bảng process_flows
step_methods: khai báo danh sách các phương thức trong một step
Coding chi tiết
Oke giờ mình sẽ đi vào chi tiết, dựng project và code các API cụ thể như sau:
1: API khởi tạo flow tương ứng với từng user
2: API xác thực giao dịch bằng phương thức PASSWORD
3: API xác thực giao dịch bằng phương thức BIOMETRIC
4: API xác thực giao dịch bằng phương thức OTP
Khởi tạo project thông qua Spring Initializr

Add thêm một số dependency trước để khởi tạo dự án, thiếu gì thì mình sẽ thêm vào sau.
Cấu trúc project mình thiết lập như trong ảnh, giờ sẽ đi chi tiết vào từng thành phần nhé:
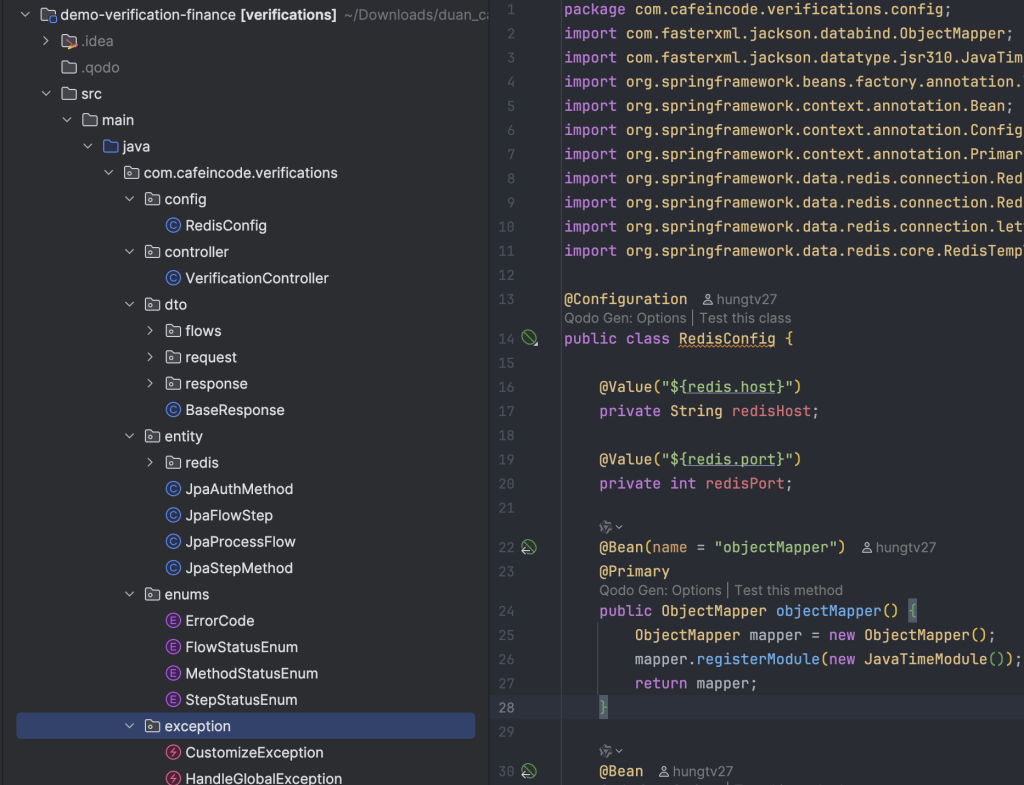
package com.cafeincode.verifications.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
/**
* @author hungtv27
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
@Bean(name = "objectMapper")
@Primary
public ObjectMapper objectMapper() {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
return mapper;
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
var config = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration(redisHost, redisPort);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(config);
}
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
var template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
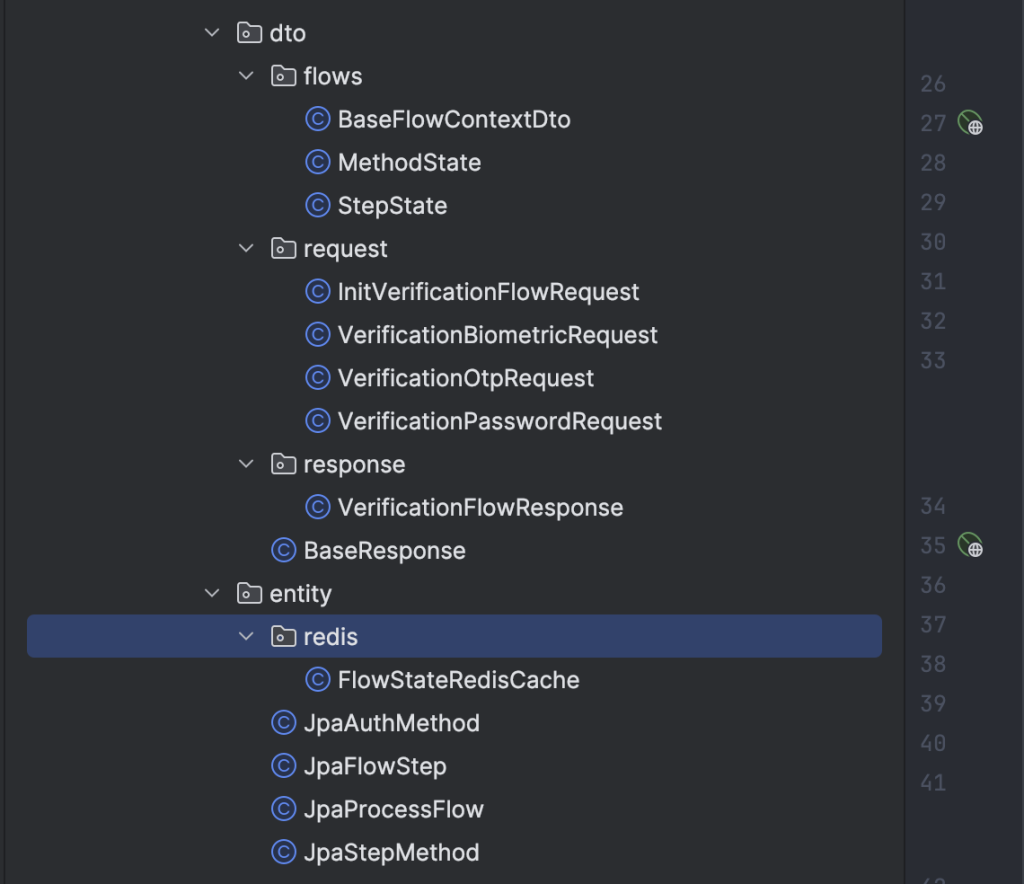
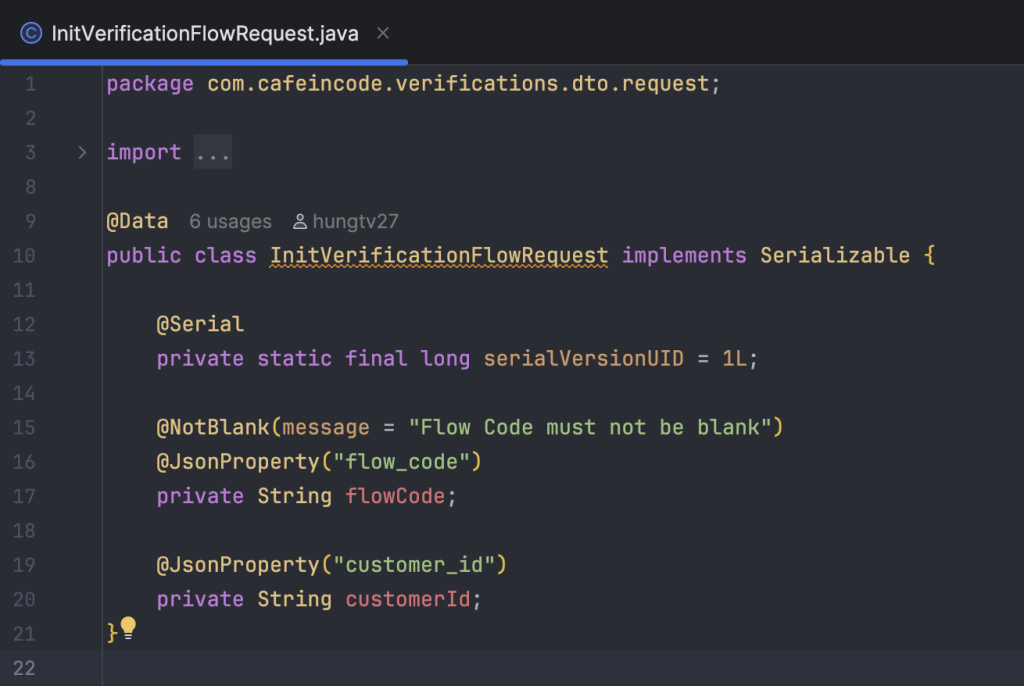
Request Body của bước khởi tạo flow, bắt buộc phải truyền flow_code.
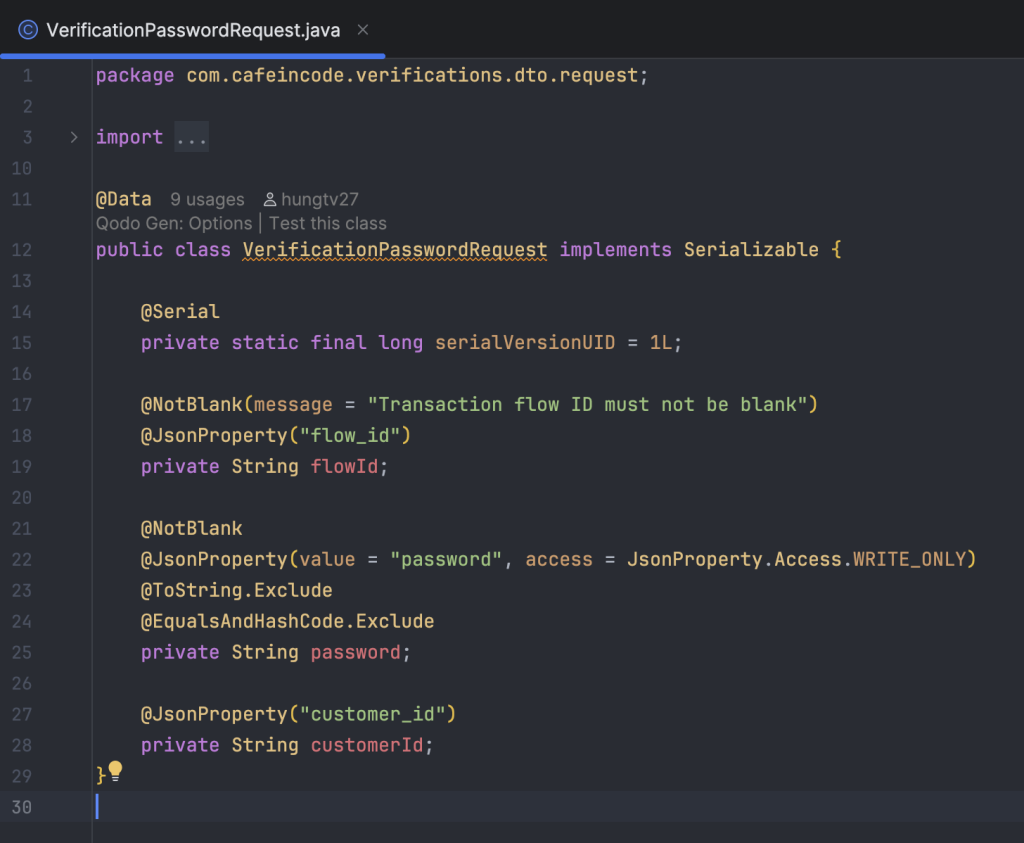
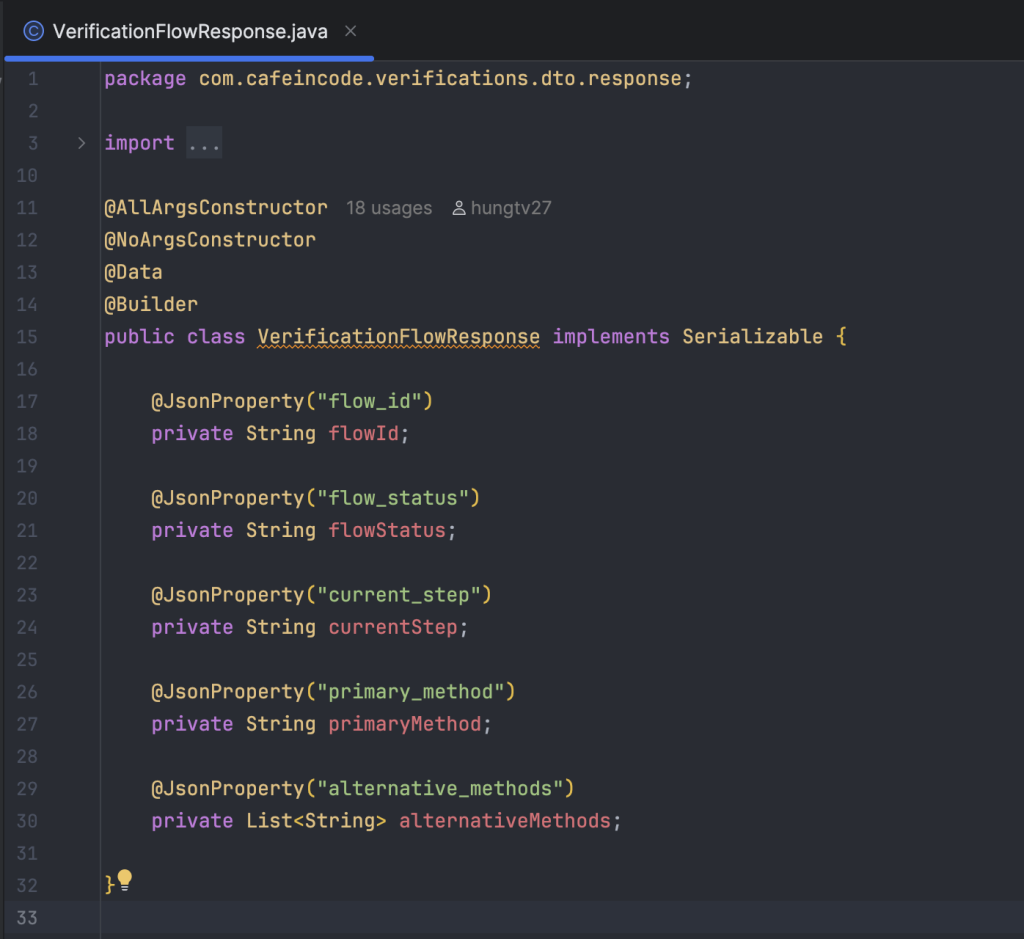
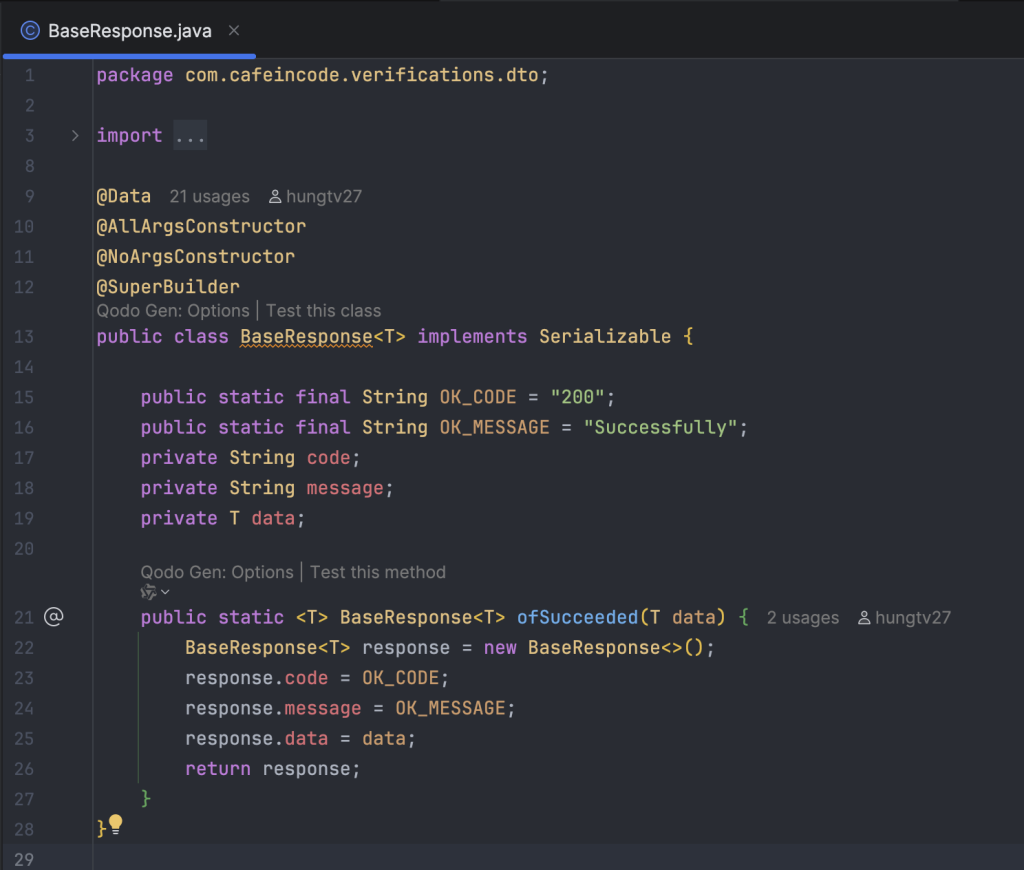
Khai báo model FlowStateRedisCache để lưu trữ danh sách flow gắn với user vào chung một Hash key là VERIFICATION_FLOW_STATE_CACHE, đặt thời gian hết hạn mặc định của Hash là 5 phút.
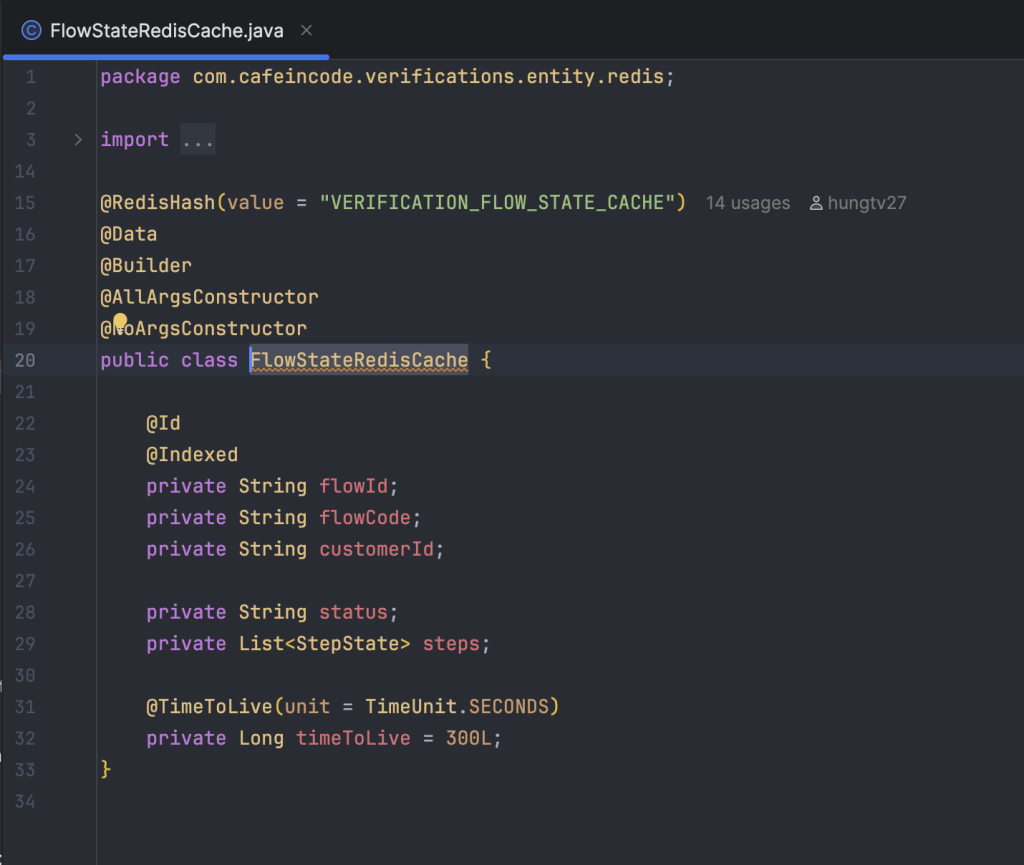
Khai báo các Enum, ErrorCode dùng chung:
package com.cafeincode.verifications.enums;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
public enum ErrorCode {
ERROR_VERIFY_METHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED("CAFEIN_275", "Verification method not supported for current step"),
ERROR_VERIFICATION_BASE_FLOW_NOT_FOUND("CAFEIN_276","Flow context not found by flow code"),
ERROR_VERIFY_FLOW_NOT_FOUND("CAFEIN_277", "Flow not found or has expired for flowId"),
ERROR_VERIFY_CUSTOMER_ID_NOT_MATCH("CAFEIN_278", "Customer ID does not match flow's customer ID"),
ERROR_VERIFY_FLOW_COMPLETED("CAFEIN_279", "Flow is already completed or has failed"),
ERROR_VERIFY_PROCESSING_STEP_NOT_FOUND("CAFEIN_280", "Find not found processing step with flowId"),
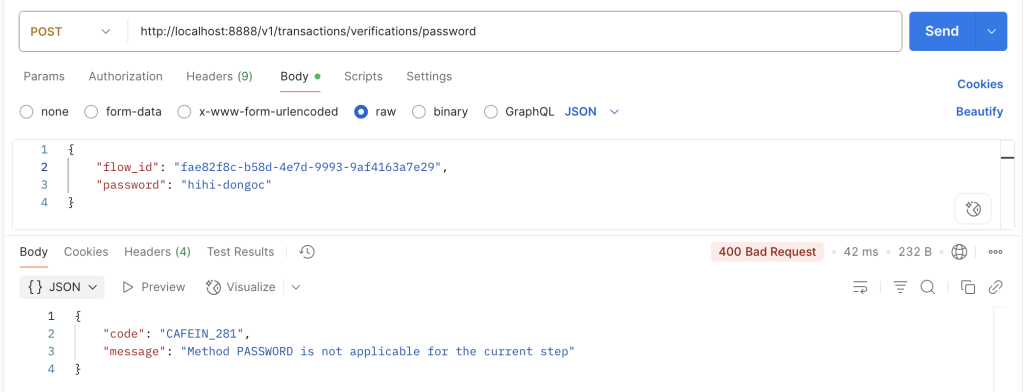
ERROR_VERIFY_PASSWORD_STEP_NOT_APPLICABLE("CAFEIN_281", "Password verification is not applicable for the current step"),
ERROR_VERIFY_PASSWORD_STEP_ALREADY_VERIFIED("CAFEIN_282", "Method already verified for current step"),
ERROR_VERIFY_BIOMETRICS_STEP_NOT_APPLICABLE("CAFEIN_283", "Biometrics verification is not applicable for the current step"),
ERROR_VERIFY_BIOMETRICS_STEP_ALREADY_VERIFIED("CAFEIN_284", "Biometrics method already verified for current step"),
ERROR_VERIFY_OTP_STEP_NOT_APPLICABLE("CAFEIN_285", "OTP verification is not applicable for the current step"),
ERROR_VERIFY_OTP_STEP_ALREADY_VERIFIED("CAFEIN_286", "OTP method already verified for current step");
private final String code;
private final String message;
}
public enum FlowStatusEnum {
IN_PROGRESS, COMPLETED;
}
public enum MethodStatusEnum {
PENDING, VERIFIED;
}
public enum StepStatusEnum {
PENDING, PROCESSING, VERIFIED;
}
Xử lý exception chung cho dự án:
package com.cafeincode.verifications.exception;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.enums.ErrorCode;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class CustomizeException extends RuntimeException {
private String code;
private String message;
private HttpStatus httpStatus;
public CustomizeException(String code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
}
public CustomizeException(ErrorCode errorCode, String message) {
this.code = errorCode.getCode();
this.message = message != null ? message : errorCode.getMessage();
httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
}
}
package com.cafeincode.verifications.exception;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class HandleGlobalException extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(CustomizeException.class)
private ResponseEntity<?> handleError(Exception ex) {
//TODO: you should custom more here
Map<String, String> body = new HashMap<>();
body.put("code", ((CustomizeException) ex).getCode());
body.put("message", ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
Tiếp tục, giờ mình sẽ khai báo các thành phần còn lại: mapper, repository, service, usecase,….
Khai báo Strategy chung cho việc xác thực các phương thức: BIOMETRIC, PASSWORD, OTP,… tức là việc xác thực các phương thức này mình sẽ đặt ở class riêng, mỗi phương thức sẽ có một cách thức xác thực khác nhau, tuỳ vào nghiệp vụ cụ thể của mỗi loại.
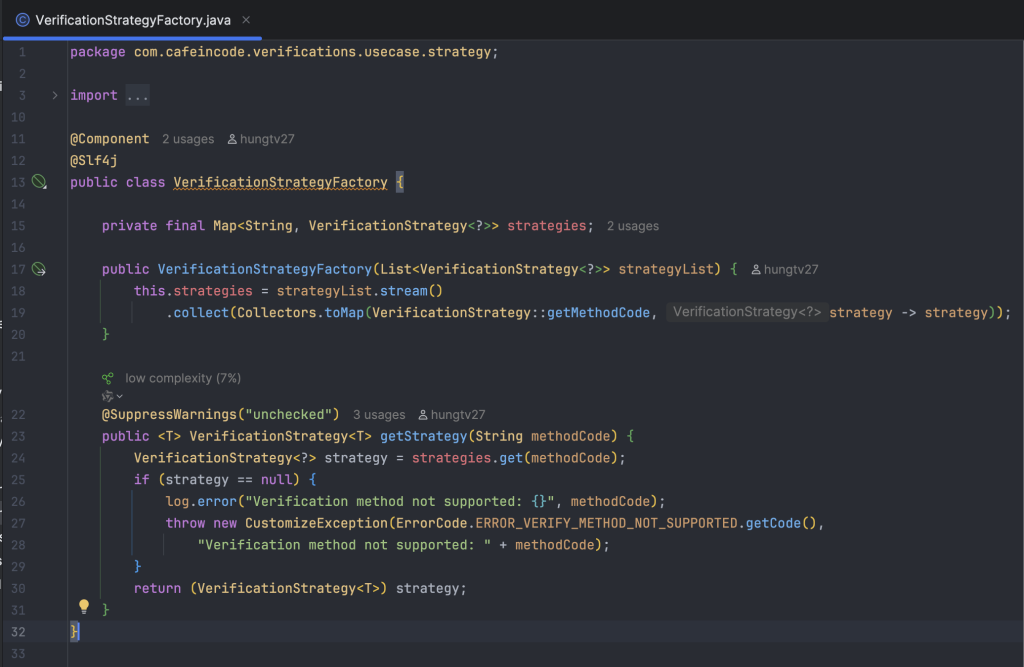
Khai báo tiếp các class implement cụ thể cho từng loại phương thức xác thực:
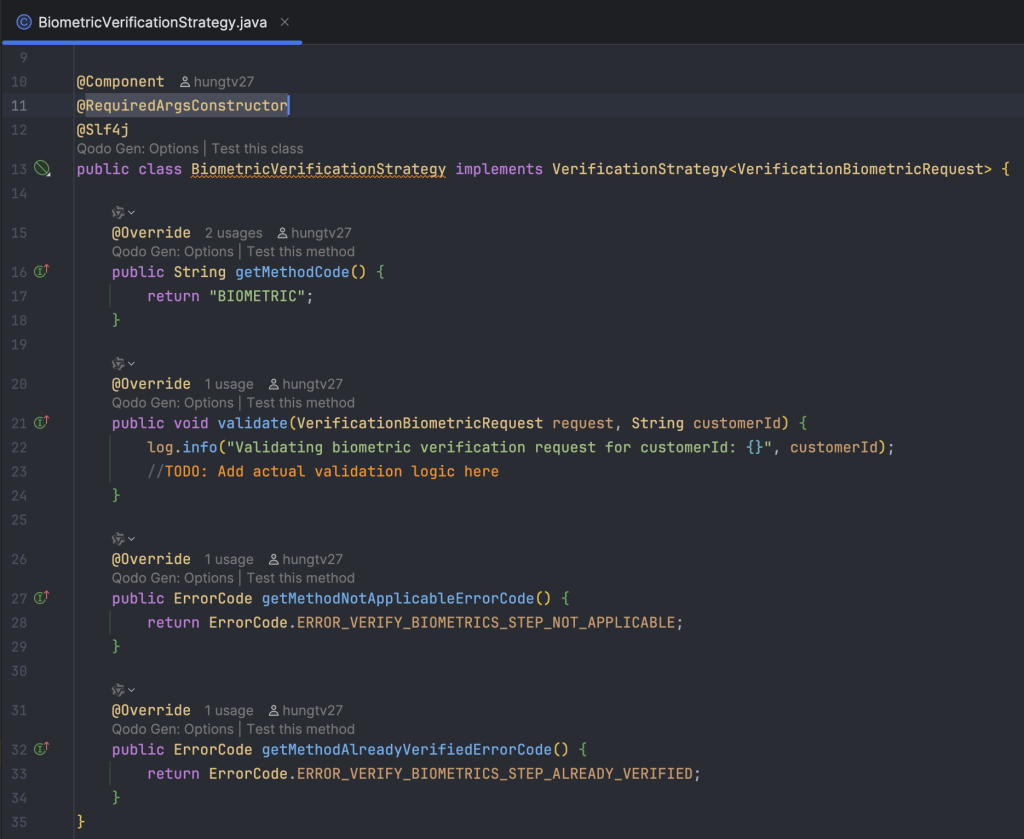
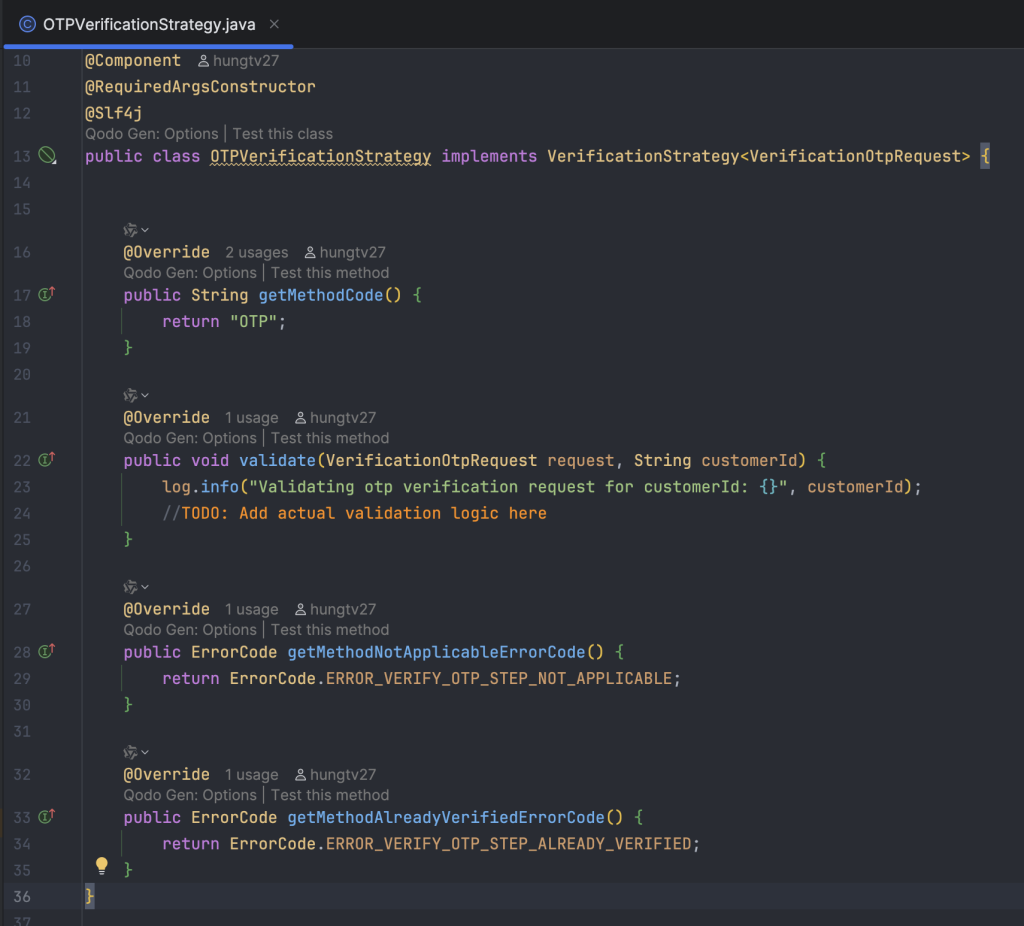
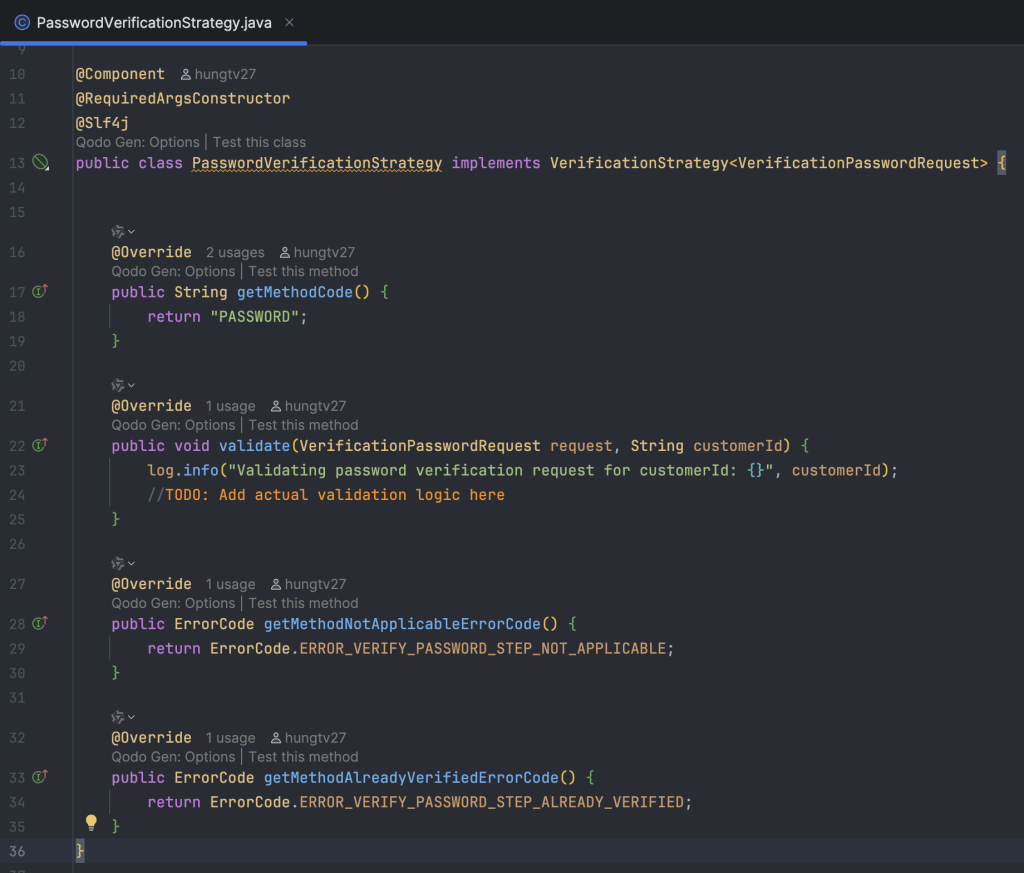
Khai báo RedisCacheService, xử lý việc build và cache lại dữ liệu của các base flow cơ bản, sẽ không gắn với một người dùng cụ thể nào ở bước này.
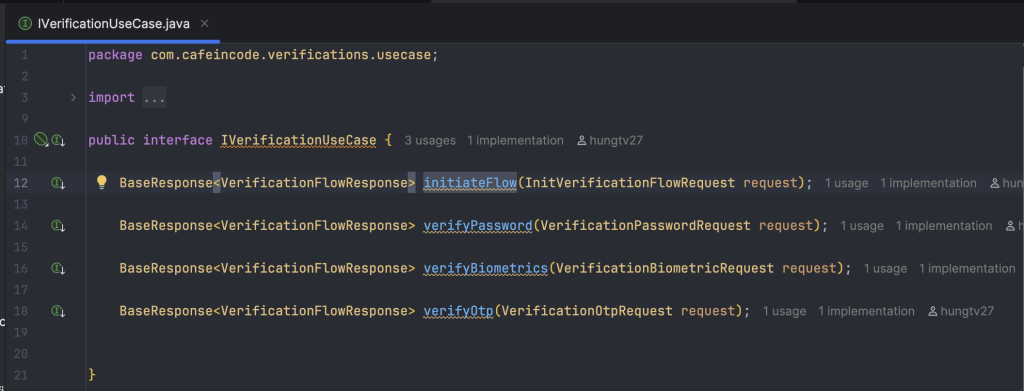
Tiếp theo, mình sẽ khai báo interface chung cho các phần nghiệp vụ quan trọng, khởi tạo flow, xác thực password, xác thực biometric, xác thực otp,…
package com.cafeincode.verifications.usecase;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.BaseResponse;
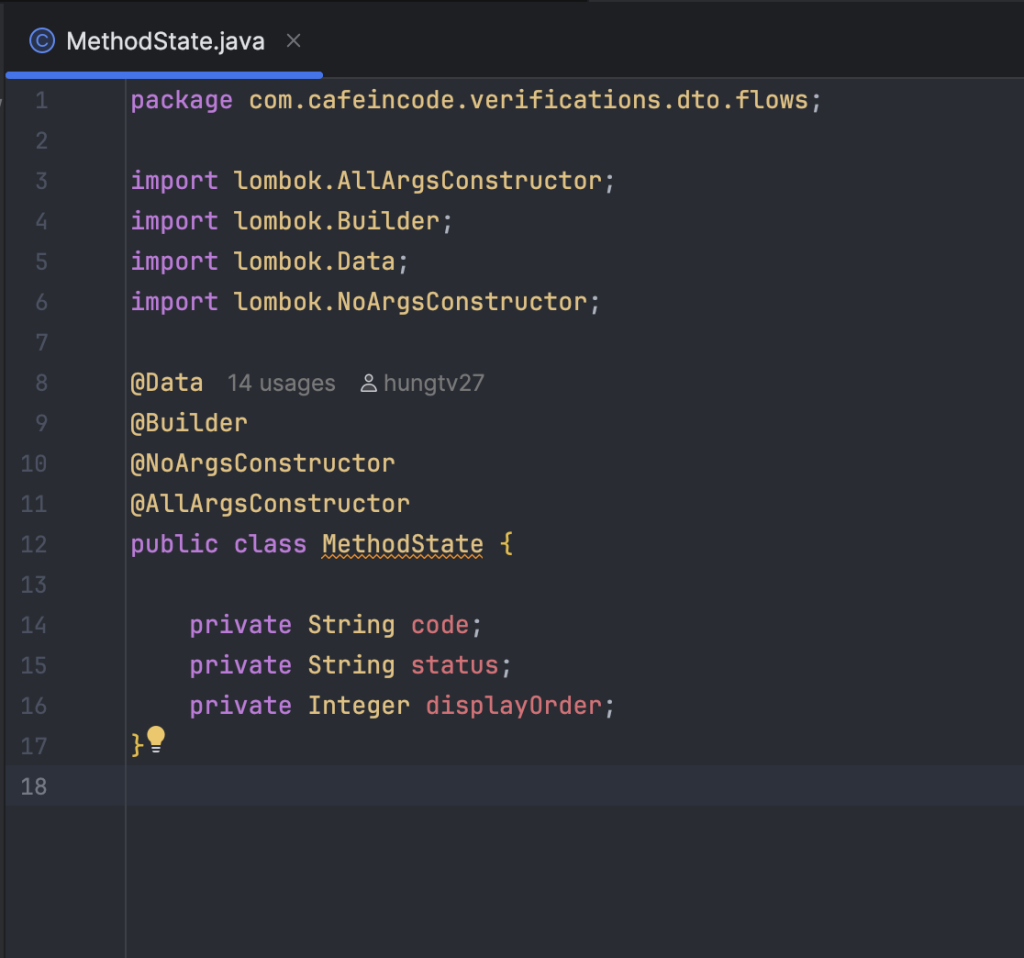
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.flows.MethodState;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.flows.StepState;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.InitVerificationFlowRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationBiometricRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationOtpRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationPasswordRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.response.VerificationFlowResponse;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.entity.redis.FlowStateRedisCache;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.enums.ErrorCode;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.enums.FlowStatusEnum;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.enums.MethodStatusEnum;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.enums.StepStatusEnum;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.exception.CustomizeException;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.mapper.VerificationMapper;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.repository.FlowStateRedisCacheRepository;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.service.RedisCacheService;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.usecase.strategy.VerificationStrategy;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.usecase.strategy.VerificationStrategyFactory;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
/**
* @author hungtv27
* cafeincode.com
*/
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class VerificationUseCase implements IVerificationUseCase {
private final VerificationMapper verificationMapper;
private final RedisCacheService redisCacheService;
private final FlowStateRedisCacheRepository flowStateRedisCacheRepository;
private final VerificationStrategyFactory verificationStrategyFactory;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> initiateFlow(InitVerificationFlowRequest request) {
var flowCode = request.getFlowCode();
var customerId = request.getCustomerId();
//1: get base flow by flow_code from Redis cache
var baseflowContext = redisCacheService.getFlowContext(flowCode);
if (baseflowContext == null) {
log.error("Flow context not found for flow code: {}", flowCode);
throw new CustomizeException(ErrorCode.ERROR_VERIFICATION_BASE_FLOW_NOT_FOUND,
"Flow context not found for flow code: " + flowCode);
}
//2: builds a new flow for user_id: hungtv27
var newFlowContext = verificationMapper.from(baseflowContext);
newFlowContext.setFlowId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
newFlowContext.setCustomerId(customerId);
newFlowContext.setStatus(FlowStatusEnum.IN_PROGRESS.name());
//3: set the first step to PROCESSING, others to PENDING
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(newFlowContext.getSteps())) {
newFlowContext.getSteps().getFirst().setStatus(StepStatusEnum.PROCESSING.name());
} else {
//4: if no steps, sets flow to COMPLETED
newFlowContext.setStatus(FlowStatusEnum.COMPLETED.name());
}
//5: persist a new flow to Redis cache: Hash key: VERIFICATION_FLOW_STATE_CACHE
var flowStateCache = flowStateRedisCacheRepository.save(newFlowContext);
//6: builds response
return BaseResponse.ofSucceeded(buildVerifyFlowResponse(flowStateCache));
}
@Override
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyPassword(VerificationPasswordRequest request) {
var strategy = verificationStrategyFactory.getStrategy("PASSWORD");
return verifyWithStrategy(request, request.getFlowId(), request.getCustomerId(), strategy);
}
@Override
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyBiometrics(VerificationBiometricRequest request) {
var strategy = verificationStrategyFactory.getStrategy("BIOMETRIC");
return verifyWithStrategy(request, request.getFlowId(), request.getCustomerId(), strategy);
}
@Override
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyOtp(VerificationOtpRequest request) {
var strategy = verificationStrategyFactory.getStrategy("OTP");
return verifyWithStrategy(request, request.getFlowId(), request.getCustomerId(), strategy);
}
private <T> BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyWithStrategy(T request, String flowId, String customerId,
VerificationStrategy<T> strategy) {
var flowState = validateFlowState(flowId, customerId);
var currentStep = getCurrentProcessingStep(flowState, flowId);
var methodToVerify = findMethodToVerify(currentStep, strategy.getMethodCode(),
strategy.getMethodNotApplicableErrorCode());
validateMethodNotAlreadyVerified(methodToVerify, flowId, strategy.getMethodAlreadyVerifiedErrorCode());
//TODO: actual verification via external service or internal logic
strategy.validate(request, customerId);
updateFlowStateAfterSuccess(flowState, currentStep, methodToVerify);
flowStateRedisCacheRepository.save(flowState);
return BaseResponse.ofSucceeded(buildVerifyFlowResponse(flowState));
}
private FlowStateRedisCache validateFlowState(String flowId, String customerId) {
var flowState = flowStateRedisCacheRepository.findById(flowId)
.orElseThrow(() -> {
log.warn("Flow state not found for flowId: {}", flowId);
return new CustomizeException(ErrorCode.ERROR_VERIFY_FLOW_NOT_FOUND,
"Flow state not found or expired for flowId: " + flowId);
});
if (!customerId.equalsIgnoreCase(flowState.getCustomerId())) {
throw new CustomizeException(ErrorCode.ERROR_VERIFY_CUSTOMER_ID_NOT_MATCH,
"Customer ID does not match for flowId: " + flowId);
}
if (!FlowStatusEnum.IN_PROGRESS.name().equalsIgnoreCase(flowState.getStatus())) {
log.warn("Attempt to verify a non-in-progress flow. Status: {}, FlowId: {}", flowState.getStatus(), flowId);
throw new CustomizeException(ErrorCode.ERROR_VERIFY_FLOW_COMPLETED,
"Flow is already completed or has failed");
}
return flowState;
}
private StepState getCurrentProcessingStep(FlowStateRedisCache flowState, String flowId) {
return flowState.getSteps().stream()
.filter(step -> StepStatusEnum.PROCESSING.name().equalsIgnoreCase(step.getStatus()))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> {
log.warn("CRITICAL: In-progress flow has no processing step with flowId: {}", flowId);
return new CustomizeException(ErrorCode.ERROR_VERIFY_PROCESSING_STEP_NOT_FOUND,
"Find not found processing step with flowId: " + flowId);
});
}
private MethodState findMethodToVerify(StepState currentStep, String methodCode, ErrorCode errorCode) {
return currentStep.getMethods().stream()
.filter(method -> methodCode.equalsIgnoreCase(method.getCode()))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomizeException(errorCode,
"Method " + methodCode + " is not applicable for the current step"));
}
private void validateMethodNotAlreadyVerified(MethodState methodToVerify, String flowId, ErrorCode errorCode) {
if (MethodStatusEnum.VERIFIED.name().equalsIgnoreCase(methodToVerify.getStatus())) {
log.warn("Method already verified for flowId: {}", flowId);
throw new CustomizeException(errorCode,
"Method already verified for flowId: " + flowId);
}
}
private void updateFlowStateAfterSuccess(FlowStateRedisCache flowState, StepState currentStep,
MethodState verifiedMethod) {
verifiedMethod.setStatus(MethodStatusEnum.VERIFIED.name());
if (checkStepCompletion(currentStep)) {
currentStep.setStatus(StepStatusEnum.VERIFIED.name());
var nextStep = findNextStepOfState(flowState, currentStep.getStepOrder());
if (nextStep != null) {
nextStep.setStatus(StepStatusEnum.PROCESSING.name());
} else {
flowState.setStatus(FlowStatusEnum.COMPLETED.name());
}
}
}
private boolean checkStepCompletion(StepState step) {
return switch (step.getFulfillmentRule().toUpperCase()) {
case "VERIFY_ONE" -> step.getMethods().stream()
.anyMatch(method -> MethodStatusEnum.VERIFIED.name().equalsIgnoreCase(method.getStatus()));
case "VERIFY_ALL" -> step.getMethods().stream()
.allMatch(method -> MethodStatusEnum.VERIFIED.name().equalsIgnoreCase(method.getStatus()));
default -> false;
};
}
private StepState findNextStepOfState(FlowStateRedisCache flowState, int currentOrder) {
return flowState.getSteps().stream()
.filter(step -> step.getStepOrder() > currentOrder)
.min(Comparator.comparing(StepState::getStepOrder))
.orElse(null);
}
private VerificationFlowResponse buildVerifyFlowResponse(FlowStateRedisCache flowStateCache) {
var result = VerificationFlowResponse.builder()
.flowId(flowStateCache.getFlowId())
.flowStatus(flowStateCache.getStatus())
.build();
if (!FlowStatusEnum.IN_PROGRESS.name().equalsIgnoreCase(flowStateCache.getStatus())) {
return result;
}
return flowStateCache.getSteps()
.stream()
.filter(step -> StepStatusEnum.PROCESSING.name().equalsIgnoreCase(step.getStatus()))
.findFirst()
.map(currentStep -> {
result.setCurrentStep(currentStep.getStepName());
var pendingMethods = currentStep.getMethods().stream()
.filter(method -> MethodStatusEnum.PENDING.name().equalsIgnoreCase(method.getStatus()))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(MethodState::getDisplayOrder))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(pendingMethods)) {
log.warn("Processing step has no pending methods for flowId: {}", flowStateCache.getFlowId());
return result;
}
result.setPrimaryMethod(pendingMethods.getFirst().getCode());
if (pendingMethods.size() > 1) {
result.setAlternativeMethods(pendingMethods.stream()
.skip(1)
.map(MethodState::getCode)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
return result;
})
.orElseGet(() -> {
log.warn("Processing step not found for flowId: {}", flowStateCache.getFlowId());
return result;
});
}
}package com.cafeincode.verifications.controller;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.BaseResponse;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.InitVerificationFlowRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationBiometricRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationOtpRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.request.VerificationPasswordRequest;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.response.VerificationFlowResponse;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.usecase.IVerificationUseCase;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author hungtv27
* cafeincode.com
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1/transactions/verifications")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class VerificationController {
private final IVerificationUseCase verificationUseCase;
@PostMapping("/flows/init")
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> initVerificationFlow(
@Valid @RequestBody InitVerificationFlowRequest request) {
var customerId = "hungtv27";
request.setCustomerId(customerId);
return verificationUseCase.initiateFlow(request);
}
@PostMapping("/password")
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyPassword(
@Valid @RequestBody VerificationPasswordRequest request) {
var customerId = "hungtv27";
request.setCustomerId(customerId);
return verificationUseCase.verifyPassword(request);
}
@PostMapping("/biometrics")
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyBiometricsDevice(
@Valid @RequestBody VerificationBiometricRequest request) {
var customerId = "hungtv27";
request.setCustomerId(customerId);
return verificationUseCase.verifyBiometrics(request);
}
@PostMapping("/otp")
public BaseResponse<VerificationFlowResponse> verifyOtp(
@Valid @RequestBody VerificationOtpRequest request) {
var customerId = "hungtv27";
request.setCustomerId(customerId);
return verificationUseCase.verifyOtp(request);
}
}Hiện tại việc cấu hình, implement code đã xong, giờ mình sẽ bổ sung thêm config dữ liệu trong database, sau đó sẽ mô tả luồng hoạt động của toàn bộ dự án.
Dữ liệu tại các bảng auth_methods, process_flows, flow_steps, step_methods được mình cấu hình như ảnh bên dưới:
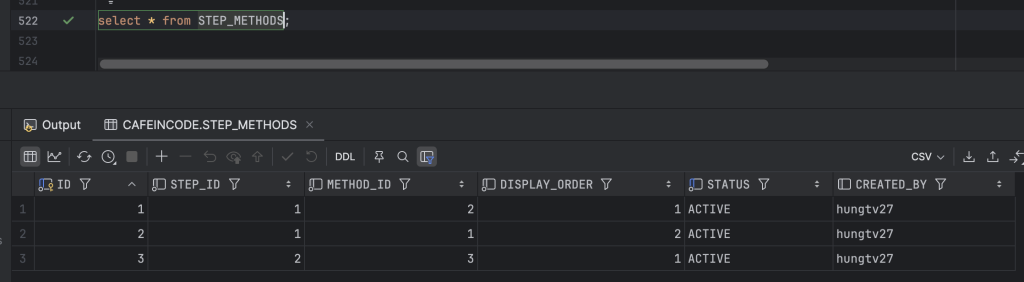
Các bạn xem code trong class RedisCacheService để hiểu cách thức thực hiện nhé, về tư tưởng sẽ là dựa trên từng bản ghi của bảng PROCESS_FLOWS, sau đó build ra cấu trúc cho từng bản ghi theo flow_code (flow_code sẽ làm key bên trong Hash Redis), rồi sau đó sẽ lưu lại toàn bộ những flow_code này vào trong Hash của Redis với key là CAFEINCODE:FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_KEY.
package com.cafeincode.verifications.service;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.flows.BaseFlowContextDto;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.flows.BaseFlowContextDto.Method;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.dto.flows.BaseFlowContextDto.Step;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.entity.JpaAuthMethod;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.entity.JpaFlowStep;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.entity.JpaProcessFlow;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.entity.JpaStepMethod;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.repository.JpaAuthMethodRepository;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.repository.JpaFlowStepRepository;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.repository.JpaProcessFlowRepository;
import com.cafeincode.verifications.repository.JpaStepMethodRepository;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import io.micrometer.common.util.StringUtils;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisCacheService {
private final RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final JpaAuthMethodRepository jpaAuthMethodRepository;
private final JpaProcessFlowRepository jpaProcessFlowRepository;
private final JpaFlowStepRepository jpaFlowStepRepository;
private final JpaStepMethodRepository jpaStepMethodRepository;
private static final String FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_CACHE_KEY = "CAFEINCODE:FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_KEY";
private static final String DEFAULT_STEP_STATUS = "PENDING";
@PostConstruct
private void initStoreVerificationFlowContext() {
var flowContextMap = initCacheFlowContext();
log.info("Built Flow Context map for {} flows, Storing to shared Redis cache...", flowContextMap.size());
storeFlowContexts(flowContextMap);
}
public Map<String, BaseFlowContextDto> initCacheFlowContext() {
var allVerificationMethods = jpaAuthMethodRepository.findByStatus("ACTIVE");
var allProcessFlows = jpaProcessFlowRepository.findByStatus("ACTIVE");
var allFlowSteps = jpaFlowStepRepository.findByStatus("ACTIVE");
var allFlowStepMethods = jpaStepMethodRepository.findByStatus("ACTIVE");
var methodMapById = allVerificationMethods.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(JpaAuthMethod::getId, Function.identity()));
var stepsByProcessFlowId = allFlowSteps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(JpaFlowStep::getProcessFlowId));
var methodsByStepId = allFlowStepMethods.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(JpaStepMethod::getStepId));
return allProcessFlows.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
JpaProcessFlow::getFlowCode,
processFlow -> buildFlowContext(processFlow, stepsByProcessFlowId, methodsByStepId, methodMapById)
));
}
private BaseFlowContextDto buildFlowContext(
JpaProcessFlow processFlow,
Map<Long, List<JpaFlowStep>> stepsByProcessFlowId,
Map<Long, List<JpaStepMethod>> methodsByStepId,
Map<Long, JpaAuthMethod> methodMapById) {
var jpaSteps = stepsByProcessFlowId.getOrDefault(processFlow.getId(), Collections.emptyList());
var steps = jpaSteps.stream()
.map(step -> buildStep(step, methodsByStepId, methodMapById))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Step::getStepOrder))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return BaseFlowContextDto.builder()
.flowCode(processFlow.getFlowCode())
.steps(steps)
.build();
}
private BaseFlowContextDto.Step buildStep(JpaFlowStep step,
Map<Long, List<JpaStepMethod>> methodsByStepId,
Map<Long, JpaAuthMethod> methodMapById) {
var jpaStepMethods = methodsByStepId.getOrDefault(step.getId(), Collections.emptyList());
var methods = jpaStepMethods.stream()
.map(stepMethod -> buildMethod(stepMethod, methodMapById))
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Method::getDisplayOrder))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return BaseFlowContextDto.Step.builder()
.stepOrder(step.getStepOrder())
.stepName(step.getStepName())
.fulfillmentRule(step.getFulfillmentRule())
.status(DEFAULT_STEP_STATUS)
.methods(methods)
.build();
}
private BaseFlowContextDto.Method buildMethod(
JpaStepMethod stepMethod,
Map<Long, JpaAuthMethod> methodMapById) {
var verificationMethod = methodMapById.get(stepMethod.getMethodId());
if (verificationMethod == null) {
return null;
}
return BaseFlowContextDto.Method.builder()
.code(verificationMethod.getMethodCode())
.displayOrder(stepMethod.getDisplayOrder())
.status(DEFAULT_STEP_STATUS)
.build();
}
private void storeFlowContexts(Map<String, BaseFlowContextDto> flowContexts) {
if (flowContexts == null || flowContexts.isEmpty()) {
log.warn("Flow contexts map is empty. Nothing to store in Redis");
return;
}
log.info("Preparing to store {} flow contexts into Redis hash with key '{}'",
flowContexts.size(), FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_CACHE_KEY);
try {
Map<String, String> redisMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, BaseFlowContextDto> entry : flowContexts.entrySet()) {
var flowCode = entry.getKey();
var dto = entry.getValue();
try {
var jsonValue = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(dto);
redisMap.put(flowCode, jsonValue);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to serialize FlowContextDto for flowCode: {}", flowCode, e);
}
}
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_CACHE_KEY, redisMap);
log.info("Successfully stored {} flow contexts to Redis", redisMap.size());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("An error occurred while storing flow contexts to Redis", ex);
}
}
public BaseFlowContextDto getFlowContext(String flowCode) {
try {
var json = (String) redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(FLOW_CONTEXT_VERIFY_CACHE_KEY, flowCode);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(json)) {
return objectMapper.readValue(json, new TypeReference<>() {
});
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("Failed to get or deserialize FlowContextDto for flow code: {}", flowCode, ex);
}
log.warn("FlowContextDto not found in Redis for flowCode: {}", flowCode);
return null;
}
}Oke giờ mình sẽ bật docker (để dùng Oracle và Redis) và khởi chạy project:
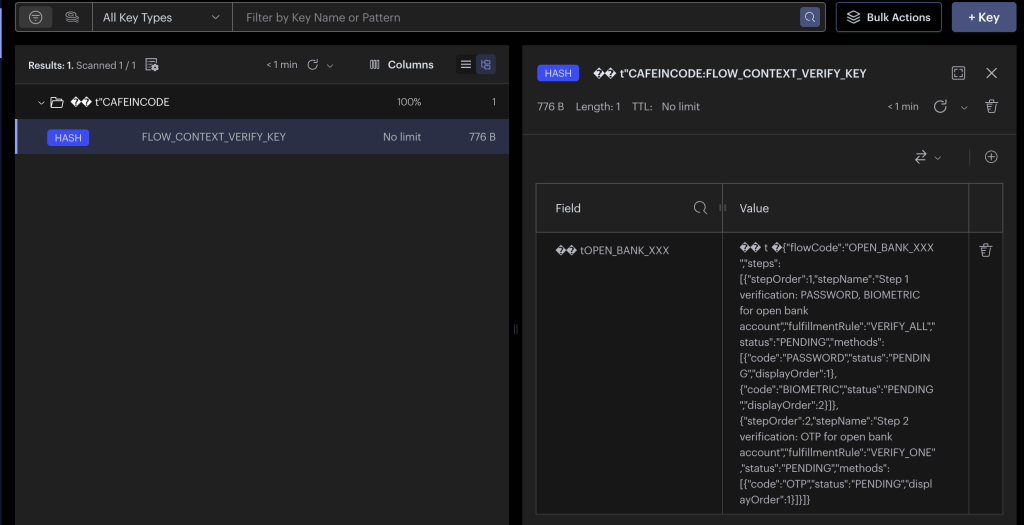
Khi chúng ta khởi chạy project, hàm initStoreVerificationFlowContext ở trong class RedisCacheService sẽ được chạy trước và xử lý một vài logic cơ bản, query database để lấy cấu hình, mapping lại dữ liệu và thực hiện việc build ra một base model cơ bản có cấu trúc JSON như sau:
{
"flowCode": "OPEN_BANK_XXX",
"steps": [
{
"stepOrder": 1,
"stepName": "Step 1 verification: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
},
{
"stepOrder": 2,
"stepName": "Step 2 verification: OTP for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "OTP",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
}
]
}
Ở đây flow_code là OPEN_BANK_XXX được gắn với hai step, step 1 có hai phương thức là PASSWORD và BIOMETRIC với rule là VERIFY_ALL, step 2 có một phương thức là OTP thôi và rule là VERIFY_ONE.
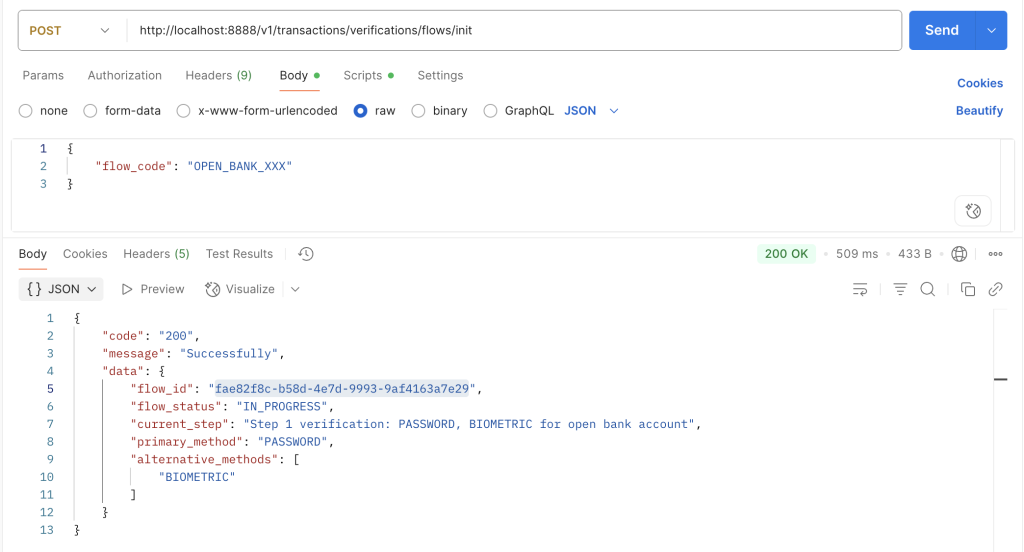
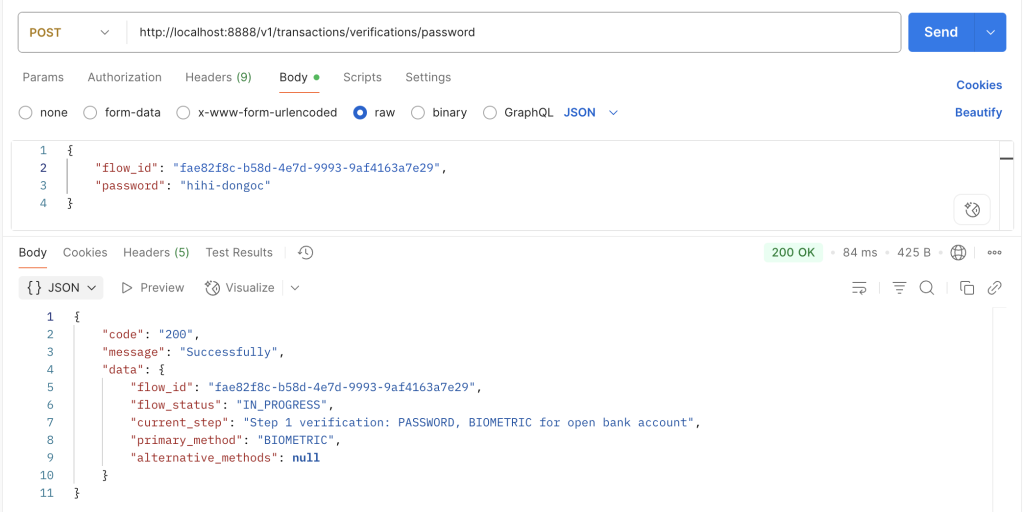
Điều này đồng nghĩa là khi chúng ta khởi tạo một flow gắn với một người dùng cụ thể (ví dụ customerId = hungtv27), thì mỗi người dùng sẽ phải thực hiện ba phương thức xác thực lần lượt là PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC và cuối cùng là OTP.
Cấu trúc của Response khi trả ra cho client mình để như sau:
{
"code": "200",
"message": "Successfully",
"data": {
"flow_id": "52bf60e3-66dd-4110-a15e-00a8d06a8059",
"flow_status": "IN_PROGRESS",
"current_step": "Step 1 verification: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC for open bank account",
"primary_method": "PASSWORD",
"alternative_methods": [
"BIOMETRIC"
]
}
}flow_id: được gắn với từng người dùng cho từng luồng nghiệp vụ khi khởi tạo, sẽ dùng flow_id cho các bước xác thực tiếp theoflow_status: là trạng thái của toàn bộ luồng flowcurrent_step: là bước hiện tại mà người dùng cần phải xác thựcprimary_method: là phương thức xác thực chính, client sẽ dựa vào trường này để quyết định điều hướng màn hình xác thựcalternative_methods: danh sách phương thức được thay thế cho phương thức chính
Giờ mình sẽ vào Postman để test các API nhé, vì chúng ta đang base trên cấu trúc JSON ở trên, nên lần lượt các phương thức khi trả về cho client sẽ là: PASSWORD -> BIOMETRIC -> OTP
1: Thực hiện gọi API /init để khởi tạo flow cho customer_id là hungtv27 (customer_id này mình set sẵn trong code, các bạn xem ở Controller phía trên)
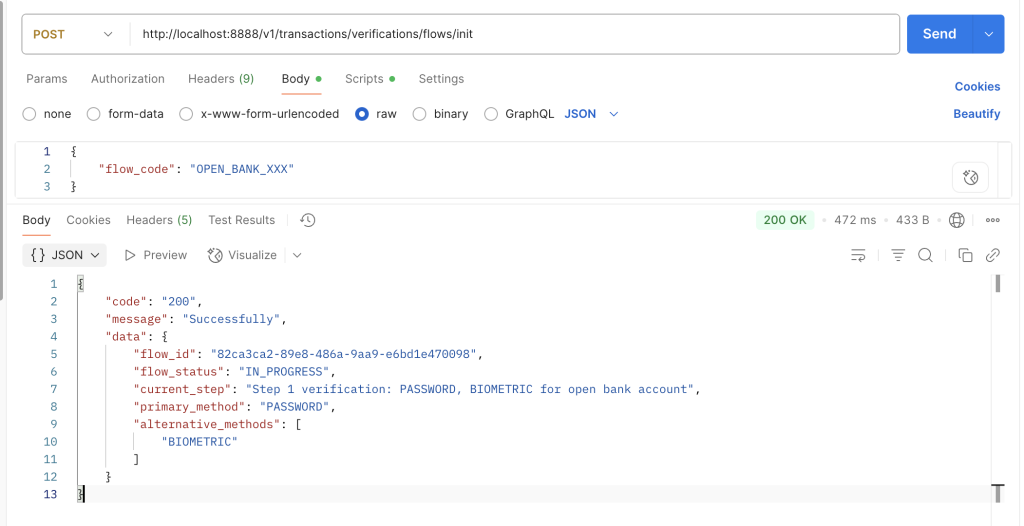
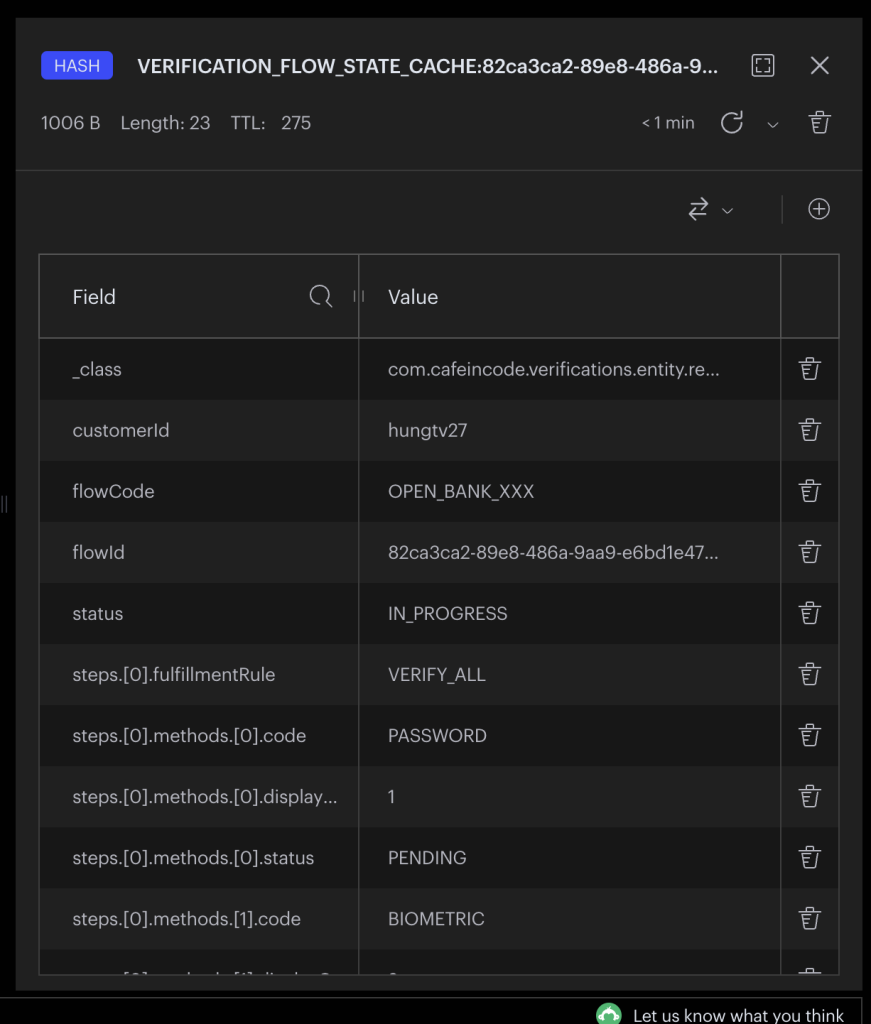
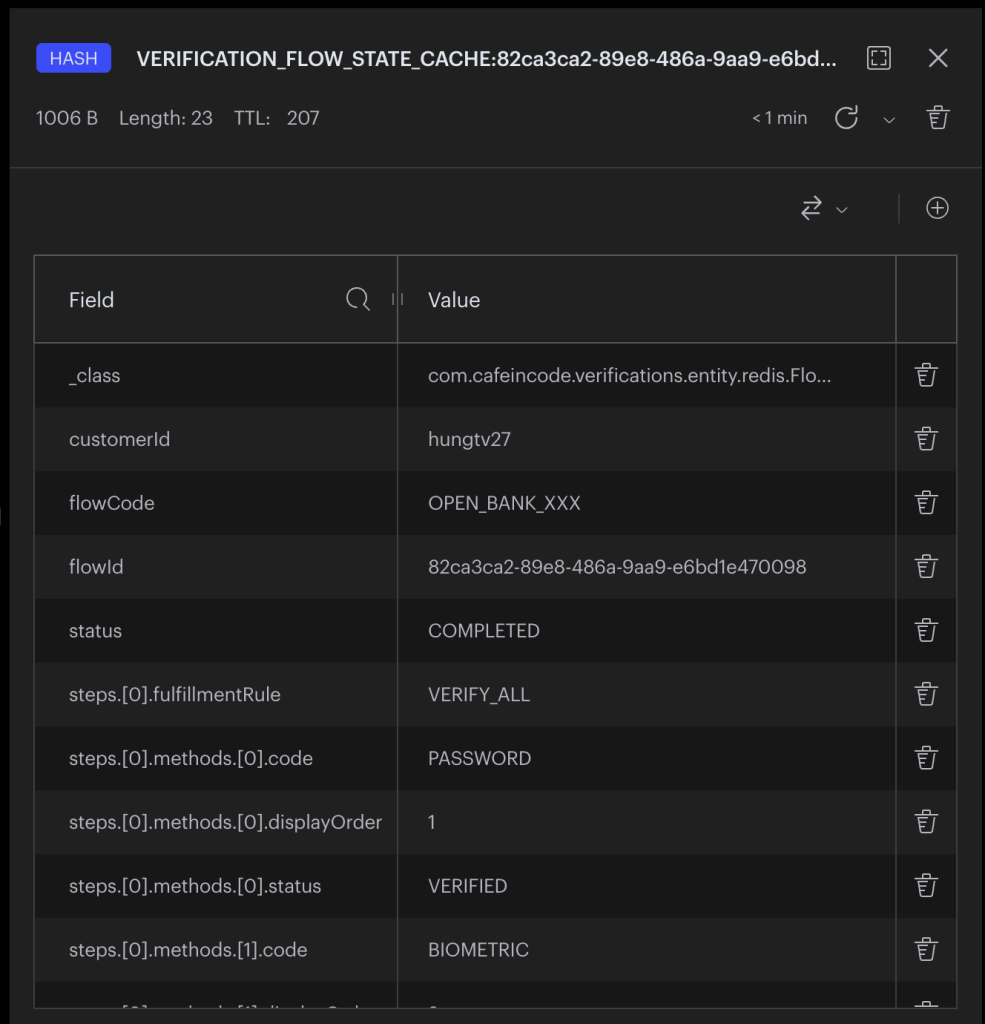
Dữ liệu trong Redis sau khi thực hiện bước init:
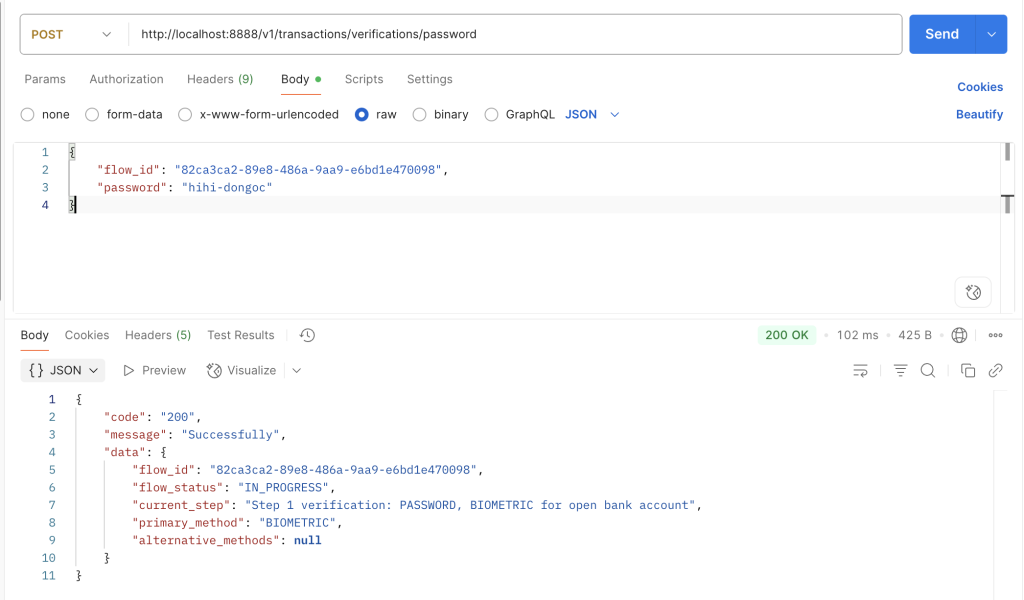
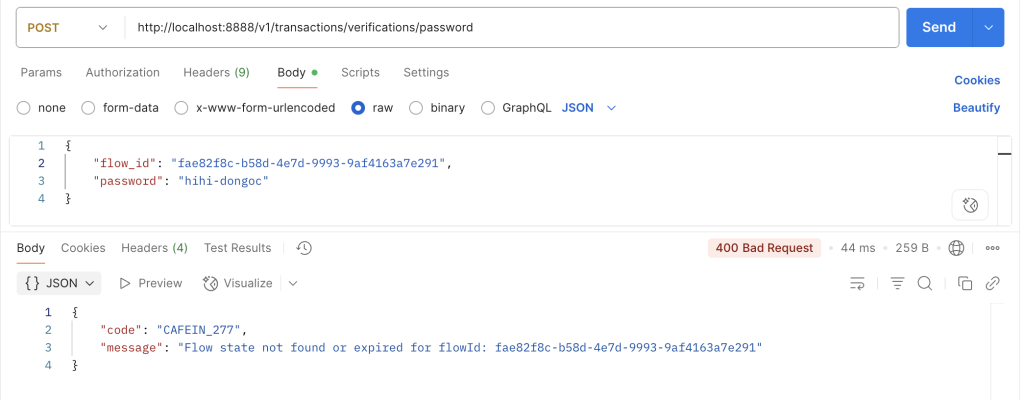
2: Phương thức nhận được lúc nãy là PASSWORD, mình thực hiện gọi API verify /password để xác thực, sau khi xác thực xong sẽ cần trả về phương thức là BIOMETRIC.
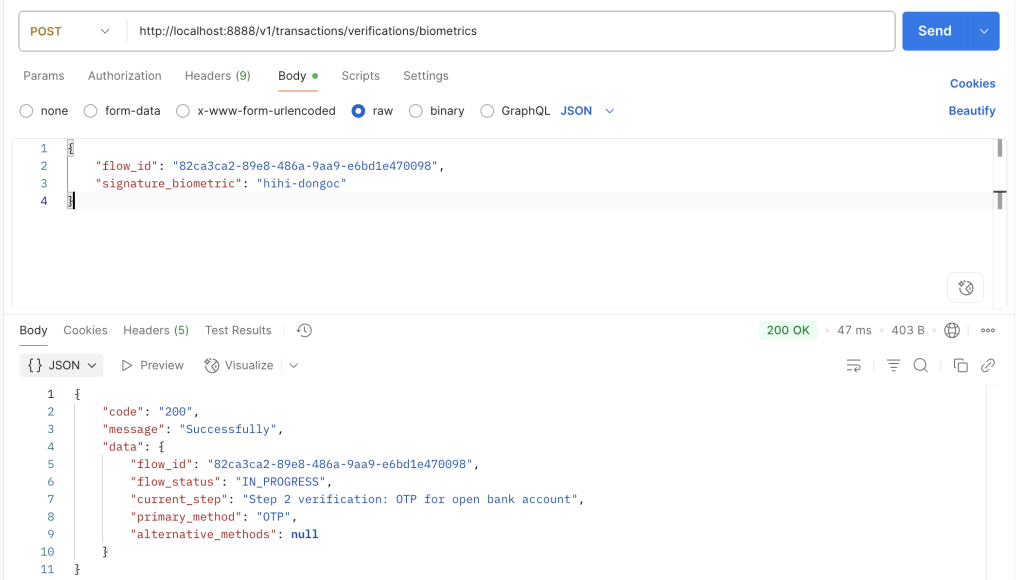
3: Tiếp tục thực hiện xác thực bằng phương thức BIOMETRIC, lúc này nếu xác thực thành công thì sẽ trả tiếp về phương thức OTP để client xác thực tiếp.
4. Thực hiện gọi API verify /otp để xác thực, lúc này nếu xác thực thành công thì luồng sẽ hoàn tất, trạng thái của luồng sẽ được đánh dấu là COMPLETED.
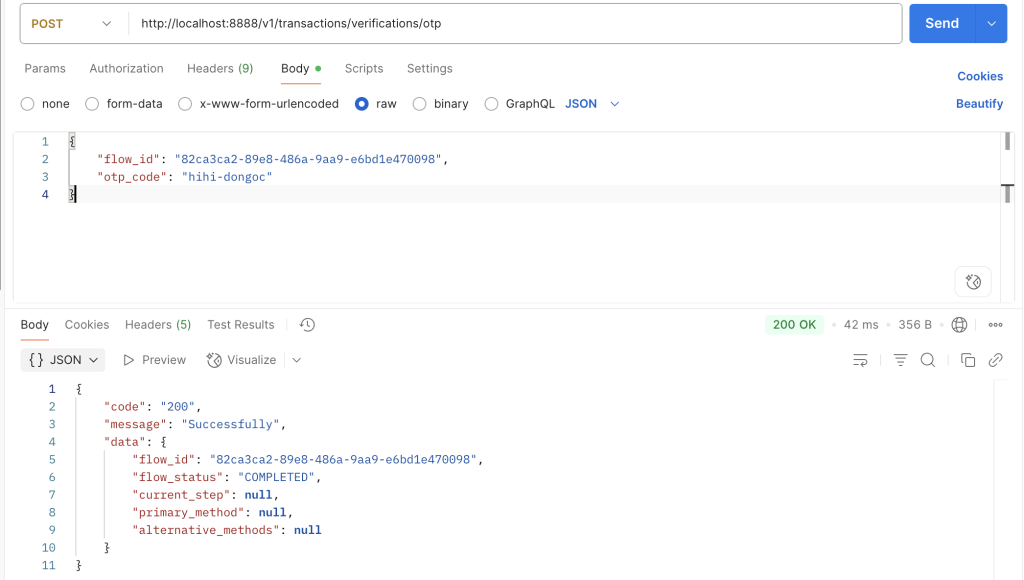
Xem lại dữ liệu bên trong Redis sau khi chúng ta thực hiện verify hoàn tất ba bước xác thực, trạng thái của luồng đã được đánh dấu là COMPLETED.
Giờ mình sẽ test thêm một số case cơ bản nữa để kiểm thử logic chính nhé:
Case 1: không tồn tại luồng xác thực
Case 2: xác thực sai bước, bước đúng là PASSWORD nhưng lại gọi phương thức OTP
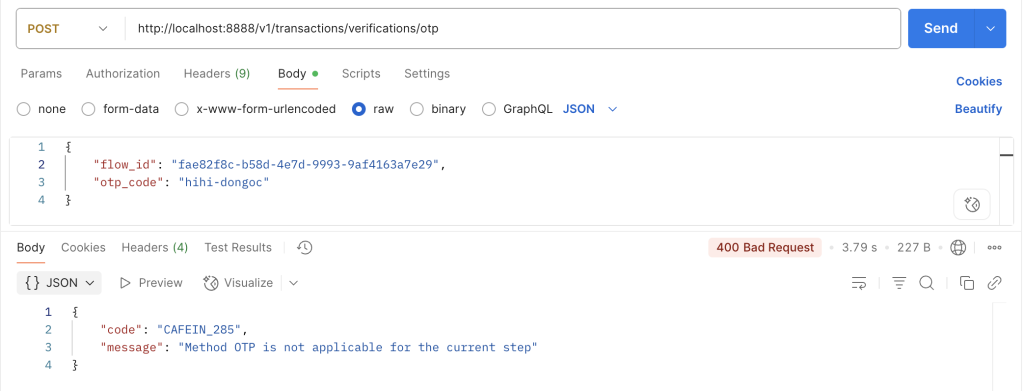
Case 3: xác thực lặp, đã xác thực PASSWORD thành công nhưng vẫn gọi lại phương thức PASSWORD
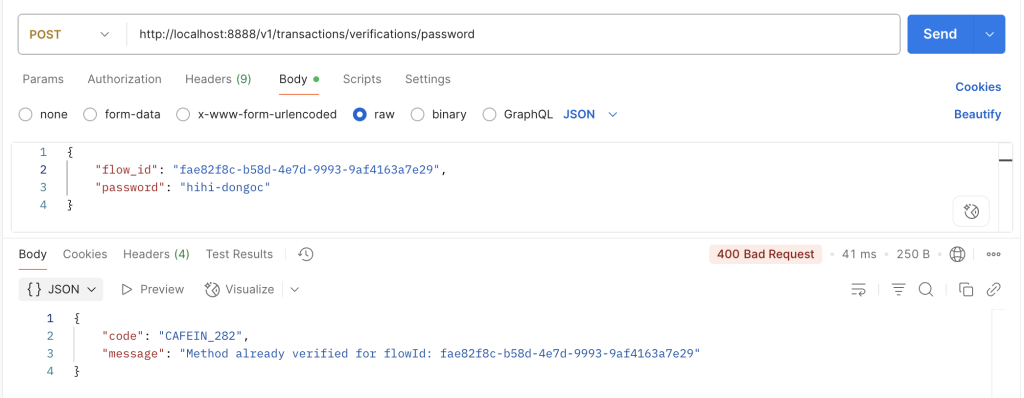
Case 4: xác thực sai phương thức của step, ví dụ step 2 phải là phương thức OTP nhưng lại gọi phương thức PASSWORD
Case 5: đã hoàn tất toàn bộ luồng rồi, nhưng vẫn thực hiện tiếp bước xác thực thì sẽ phải báo lỗi
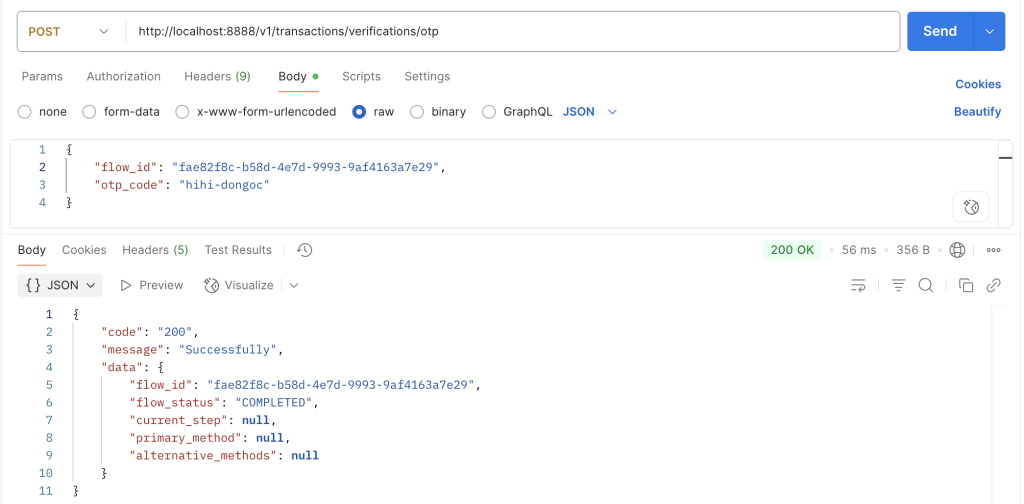
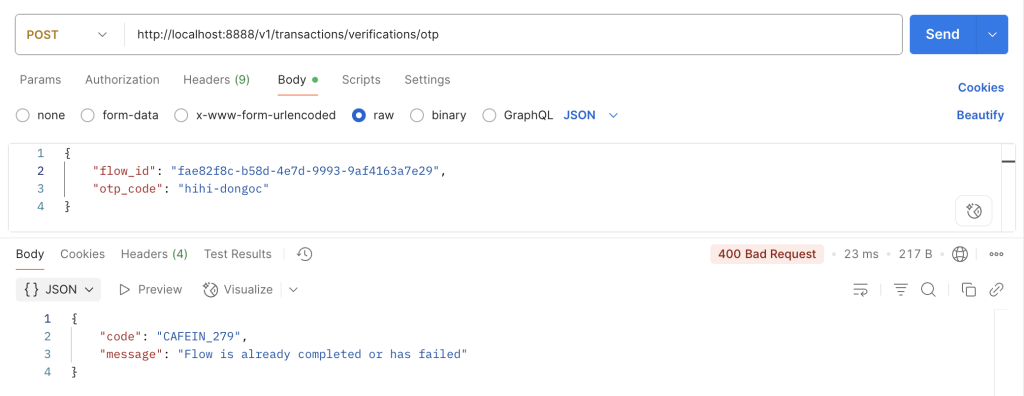
Phân tích luồng hoạt động
Cùng xem lại cấu trúc JSON bên trên để xem logic xử lý diễn ra như nào nhé các bạn:
{
"flowCode": "OPEN_BANK_XXX",
"steps": [
{
"stepOrder": 1,
"stepName": "Step 1 verification: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
},
{
"stepOrder": 2,
"stepName": "Step 2 verification: OTP for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "OTP",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
}
]
}Cấu trúc cho từng luồng nghiệp vụ sẽ được lưu như ở trên, sẽ không gắn với customer_id hoặc flow_id nào cả, mà chỉ là một cấu trúc tĩnh.
Sau đó khi thực hiện bước /init thì sẽ sinh ra tương ứng các flow gắn với user cụ thể, cấu trúc dữ liệu sẽ như sau:
{
"flowId": "d3140777-5860-40d3-a32b-425c149f6e27",
"flowCode": "OPEN_BANK_XXX",
"customerId": "hungtv27",
"status": "IN_PROGRESS",
"steps": [
{
"stepOrder": 1,
"stepName": "Step 1 verification: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "PROCESSING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
},
{
"stepOrder": 2,
"stepName": "Step 2 verification: OTP for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "PENDING",
"methods": [
{
"code": "OTP",
"status": "PENDING",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
}
],
"timeToLive": 300
}
Tiếp tục, theo như cấu trúc JSON trên, thì chúng ta sẽ phải thực hiện tuần tự các phương thức xác thực là PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC và OTP thì luồng mới hoàn tất.
Gắn với mỗi flow sẽ được đặt một giá trị timeToLive là 5 phút để tự động hết hạn.
Sau khi người dùng thực hiện phương thức xác thực là PASSWORD và BIOMETRIC xong, luồng nghiệp vụ sẽ kiểm tra xem với rule là VERIFY_ALL ở step 1 thì các phương thức đã thực sự được xác thực hay chưa (bằng cách kiểm tra trạng thái status ở trong methods).
Trong trường hợp nếu toàn bộ hai phương thức của step 1 đã hoàn thành, trạng thái của step 1 sẽ được đánh dấu VERIFIED, luồng sẽ nhảy tiếp đến step 2 và trả ra phương thức OTP để người dùng xác thực.
Sau khi xác thực OTP xong thì luồng nghiệp vụ sẽ kiểm tra tiếp, với rule là VERIFY_ONE thì đã thoả mãn rule rồi, lúc này step 2 sẽ được đánh dấu là VERIFIED, toàn bộ luồng lúc này cũng sẽ được đánh dấu là COMPLETED.
Cấu trúc JSON cuối cùng ở trong Redis sau khi toàn bộ luồng thực sự đã hoàn thành như sau:
{
"flowId": "d3140777-5860-40d3-a32b-425c149f6e27",
"flowCode": "OPEN_BANK_XXX",
"customerId": "hungtv27",
"status": "COMPLETED",
"steps": [
{
"stepOrder": 1,
"stepName": "Step 1 verification: PASSWORD, BIOMETRIC for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ALL",
"status": "VERIFIED",
"methods": [
{
"code": "PASSWORD",
"status": "VERIFIED",
"displayOrder": 1
},
{
"code": "BIOMETRIC",
"status": "VERIFIED",
"displayOrder": 2
}
]
},
{
"stepOrder": 2,
"stepName": "Step 2 verification: OTP for open bank account",
"fulfillmentRule": "VERIFY_ONE",
"status": "VERIFIED",
"methods": [
{
"code": "OTP",
"status": "VERIFIED",
"displayOrder": 1
}
]
}
],
"timeToLive": 160
}Giải pháp xác thực giao dịch đến đây đã hoàn thành rồi, các bạn có thể đem nó đi để áp dụng cho tất cả các luồng nghiệp vụ khác nhau, giờ nếu có nhu cầu chỉnh sửa hoặc thêm mới các luồng nghiệp vụ thì chỉ cần khai báo thêm hoặc cập nhật lại cấu hình trong database là ổn rồi, không cần phải code thêm gì nữa (trừ khi bổ sung thêm loại xác thực khác ví dụ SOFT_OTP, BIO_2345,…).
Trong bài viết của mình có 1 điểm nhỏ chưa tối ưu liên quan đến việc sử dụng Redis, mình định bổ sung vào nhưng bài viết đã dài quá rồi nên mình không đưa thêm vào nữa, các bạn hãy cùng đọc và tìm ra điểm chưa tối ưu đó nhé, nếu tìm ra hãy comment bên dưới bài viết cho mọi người cùng biết, chúc các bạn học và làm việc thật tốt.
Xem thêm các bài viết nổi bật bên dưới:
- Đồng nghiệp tôi vừa mới Golive và bùm, race condition
- Tổng hợp dữ liệu cho 1 triệu tài khoản trong 4 phút
- Xử lý lỗi lệch múi giờ khi dùng Mapstruct
- Có CodeRabbit làm tôi review code cũng nhàn hơn
- Lỗi trên môi trường Staging mà không ai chịu sửa đến cùng
- Filter Spring và pha xử lý bug nhớ đời
- Những thói quen tốt trong ngành phát triển phần mềm
- Viết code với những thói quen tốt này sẽ giúp bạn giỏi hơn
- Làm việc trong môi trường Agile là như thế nào
- Rest API: Cách Ngăn Chặn Duplicate Request Hiệu Quả
- Sức mạnh của AI CLI – trợ thủ đắc lực cho dân lập trình